|17-1-2017 | Arnoud Doornbos |

Since the start of the financial crisis a growing need for more bank independency with companies has arisen. Bank counterparty risk became an issue. A large cash management bank announced in 2015 to stop their transactional banking services for continental Europe. What will happen with current cash pools running with banks in the UK? Increased regulations (Basel III) may stop certain banking products.
All types of events where companies feel a growing need for more bank independency.
Basel III
In the coming years, banks have to prepare themselves for compliance with the new Basel III rules on financial institutions.
The financial crisis of 2008 brought the shortcomings of Basel II to light. The capital requirements for banks were found to be insufficient and banks were running risks which were not identified by Basel II.
Therefore the focus of Basel III is to restore previous mistakes and adding requirements to both the quality and composition of the capital held by banks and liquidity position and governance to manage the risks.
Effective liquidity management is a way to look for “Idle” cash. An increasing number of companies therefore choose for notional pooling as it enables them to gain more insight into their (global) financial position and in order to optimize the interest income on their accounts.
Simultaneously Basel III imposes stricter requirements on offsetting balances (credit and debit), and this brings notional pooling possibly into danger. The question is what impact the introduction of Basel III has to notional pooling services offered by banks.
Notional Pooling
Notional pooling is a mechanism for calculating interest on the combined credit and debit balances of accounts that a corporate parent chooses to cluster together, without actually transferring any funds between the accounts. It is ideal for companies with decentralized organizations that want to allow some autonomy to their subsidiaries, including their control over bank accounts.
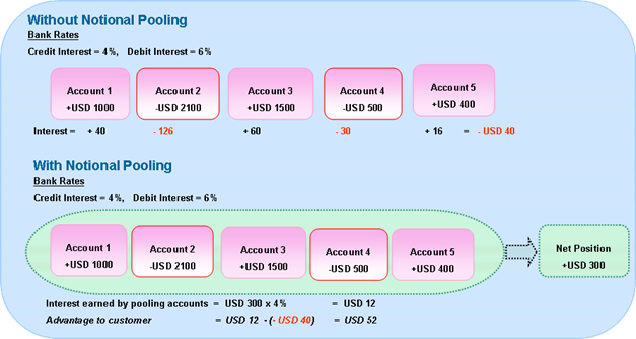
Benefits of notional pooling
The use of notional pooling has increased tremendously in recent years. At the moment it is a commonly used structure to concentrate balances and maximize the interest income on bank accounts. In addition it will provide companies with an increased understanding of their financial position and the company is therefore able to manage their money more effectively. Another commonly used technique is physical pooling (zero balancing) where the money from the participating accounts is transferred via a physical transfer to a higher-level account. The difference between them is that with notional pooling the money shall be paid only virtual and with physical pooling a physical transfer of money takes place. By using physical pooling through physical money transfer, internal debt positions will be created. Notional pooling and physical pooling can also be combined in an overlay structure.
Liquidity management
Basel III introduces a number of new financial ratios that aim to strengthen the capital base of banks.
One of the most significant ratios is the liquidity coverage ratio which banks are required to hold in high-quality liquid assets (cash money or assets which can be sold on the market quickly). This liquidity coverage ratio shows how far banks are able to withstand sufficiently a ‘crisis’ on cash flows for a period of thirty days. Moreover, the new law increases the capital requirements for banks and make these requirements more risk-weighted than before. The requirements are also countercyclical, intended to encourage banks to build up more capital in economic good times.
Liquidity management is gaining popularity by two simultaneous developments. On the one hand, credit is a less attractive source of profit for banks, which enforced banks to shift their focus to activities without capital requirements. On the other hand, companies need to make optimal use of internal cash as bank financing is becoming increasingly difficult. Notional pooling offers the option to concentrate the balances at several (international) accounts and optimize the interest.
Uncertain future for notional pooling
Basel III does not always allow that liquidity ratios are calculated by means of netting the outstanding balances of accounts in the notional pool. This means that banks must calculate their ratios based on the gross value of individual accounts. To cover the negative positions in the notional pool banks need to hold more liquidity. The negative position is seen as overdraft, which is associated with unattractive Risk Weighted Asset (RWA) for the bank. The conditions for reducing this RWA vary by bank and are depending also on the central bank of an individual country. To prevent that banks are required to hold a higher amount of risk capital they must be in possession of a legal right of offset. However, the process to obtain this right involves a lot of time and high costs (both for the bank and the company) and requires the necessary legal and tax knowledge. First, the law in the jurisdiction of each participant of the notional pool must allow compensation in the event of bankruptcy. In addition each participant of the notional pool must sign a paper that allow them to guarantee for other participants. Finally, the company must demonstrate that netting has occurred periodically.
Regarding the future of notional pooling, there are a number of scenarios to think of when it comes to the continuation of this service by banks:
- Banks will only allow entities in the notional pool if there is an enforceable right of compensation;
- Banks will charge the higher costs related to notional pooling to the companies;
- Banks offer notional pooling selectively based on the creditworthiness of the company.
If banks decide to increase the price for notional pooling, it is likely that companies will go for alternatives for their cash management activities (e.g. physical pooling). Therefore it is advisable to contact your bank regarding notional pooling, so you are not faced with unnecessary surprises.
Treasury Services monitors the developments in the Basel III framework closely and combines its expertise in the areas of Payments, Treasury and Risk in order to provide its customers the best advice.
The Treasury Services Cash Management Scan analyses the impact of Basel III on your current cash pools and will explain how to manage this in the future.
Bank independent Cash Pooling
Treasury Services has developed a solution to set up cash pooling structures completely independent from banks through software. This creates significant additional savings and advantages compared to a cash pooling solution with banks.
The bank independent cash pooling allows companies to pool different bank accounts with different banks in different countries.
The advantages are:
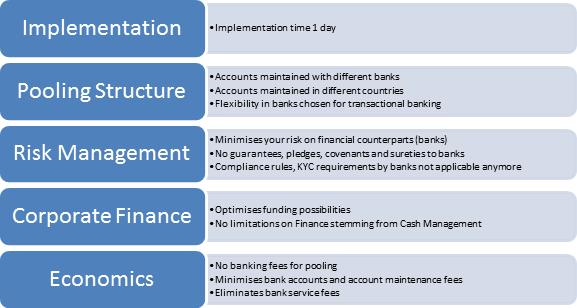
The solution we have developed is a complete solution. It does not only consist of a software solution, but also proposed changes for policies and processes, and we investigated the legal and fiscal constraints.
For more information please refer to this link.

Arnoud Doornbos
Partner at Treasury Services





 With globalisation and an increasingly complex business environment, having an efficient and centralised payment system is vital to any multinational’s success. Recognising this, we at HSBC are proud to have successfully connected to Treasury Intelligence Solutions (TIS) in Asia for automated payment and bank statement processing.
With globalisation and an increasingly complex business environment, having an efficient and centralised payment system is vital to any multinational’s success. Recognising this, we at HSBC are proud to have successfully connected to Treasury Intelligence Solutions (TIS) in Asia for automated payment and bank statement processing.




 As you may remember I travelled throughout South Africa in december 2016. Being back home I was curious to learn if there were developments in the blockchain area. A
As you may remember I travelled throughout South Africa in december 2016. Being back home I was curious to learn if there were developments in the blockchain area. A 


 Brexit is an ongoing issue in not just the financial world, but in the entire world. A topic which had lots of speculations, rumors and uncertainties. Although 2017 is going to bring us more clearness around Brexit, the exact date when Brexit is actually happening is still unknown. Theresa May, Prime Minister of the UK, said she will put Article 50 into motion by the end of March 2017. If she is able to put this article into motion, the actual process of withdrawal must be completed within two years. Anyhow, Brexit has its effects on the economy.
Brexit is an ongoing issue in not just the financial world, but in the entire world. A topic which had lots of speculations, rumors and uncertainties. Although 2017 is going to bring us more clearness around Brexit, the exact date when Brexit is actually happening is still unknown. Theresa May, Prime Minister of the UK, said she will put Article 50 into motion by the end of March 2017. If she is able to put this article into motion, the actual process of withdrawal must be completed within two years. Anyhow, Brexit has its effects on the economy. PowerToPay
PowerToPay Prior to the sale of an SME, the shareholder/director is often advised to make early steps to prepare for a business transfer. This would increase the value at the moment of the sale, thus resulting in higher proceeds from this sale. At this point, many questions arise, like ‘what should be done?’, ‘how does this work?’ and ‘what are expected results?’. The lack of clear answers is a major cause for not making right choices and taking adequate steps in practice. Which leads to disappointing outcomes at the time of sale. Timely preparation for a business transfer is supported by four major pillars: working capital management, investment policy, cost effectiveness and business rigidity. My third book, titled “Werken aan Waardestuwers? Over waarde en klinkende munt!” (in Dutch) is about this topic.
Prior to the sale of an SME, the shareholder/director is often advised to make early steps to prepare for a business transfer. This would increase the value at the moment of the sale, thus resulting in higher proceeds from this sale. At this point, many questions arise, like ‘what should be done?’, ‘how does this work?’ and ‘what are expected results?’. The lack of clear answers is a major cause for not making right choices and taking adequate steps in practice. Which leads to disappointing outcomes at the time of sale. Timely preparation for a business transfer is supported by four major pillars: working capital management, investment policy, cost effectiveness and business rigidity. My third book, titled “Werken aan Waardestuwers? Over waarde en klinkende munt!” (in Dutch) is about this topic.
 Het blijft een terugkerend thema als meerdere treasurers samenkomen of als ik over loopbaanplanning spreek: is blijven in treasury een recept voor vastlopen in je carrière? Bouw je door op hetgeen je hebt bereikt of doe je een stap terug/opzij om er weer twee vooruit te maken? Zonder uitputtend te willen zijn zal ik veel genoemde reacties beschrijven.
Het blijft een terugkerend thema als meerdere treasurers samenkomen of als ik over loopbaanplanning spreek: is blijven in treasury een recept voor vastlopen in je carrière? Bouw je door op hetgeen je hebt bereikt of doe je een stap terug/opzij om er weer twee vooruit te maken? Zonder uitputtend te willen zijn zal ik veel genoemde reacties beschrijven. In
In  Annette Gillhart – Community Manager treasuryXL
Annette Gillhart – Community Manager treasuryXL