3 tips for a successful accounting- and ERP-system roll-out
| 23-3-2017 | Christian van Ledden | Sponsored content |

Cloud based accounting- and ERP-systems, i.e. SAP S4-HANA are receiving a lot of attention these days. The result? – Increasingly more companies are considering cloud solutions in their effort to consolidate IT processes and systems. According to a study by Panorama Consulting, in 2015 the share of such ERP-systems increased from 4% in 2014 to 33%.
Cloud is here to stay
From our point of view, this development is primarily driven by two factors: on the one hand, the amount of mature solutions in the marketplace is growing. At the same time, cloud ERP-systems are being positioned more aggressively by their respective vendors. On the other hand, there is a common acceptance of cloud ERP-systems. This is underlined by a study from RightScale, according to which 82% of companies are employing a multi-cloud strategy in 2015, up from 74% in 2014.
The former can also be observed in the cloud revenue figures of SAP and Oracle: SAP increased its revenue from cloud products and services between 2013 and 2015 by a staggering 229% while Oracle recorded similar growth in its cloud segment of 100% over the same period. Oracle’s strategic focus on cloud business is underlined by its recent acquisition of Netsuite.
This development has major advantages for their respective clients. According to a study by the Aberdeen Group, corporates can improve their operating profit margin by up to 21% through implementation of a modern cloud ERP-system. These improvements are achieved through optimized processes, higher standardization as well as a more streamlined IT environment.
Fast implementation and cost savings by using the TIS payment solution
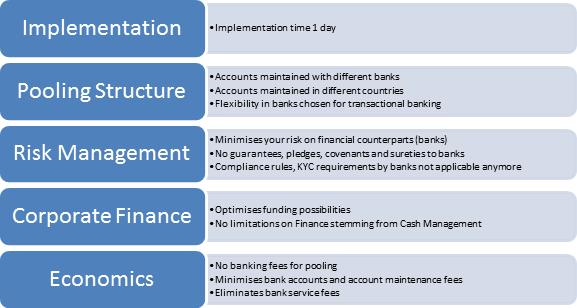
The majority of finance and treasury departments are in one way or another affected by the roll-out of a new ERP-system. Generally, the aim is to standardize processes and systems. This brings its own set of IT-related challenges. These can be split into three major categories: processes, connectivity, and change management.
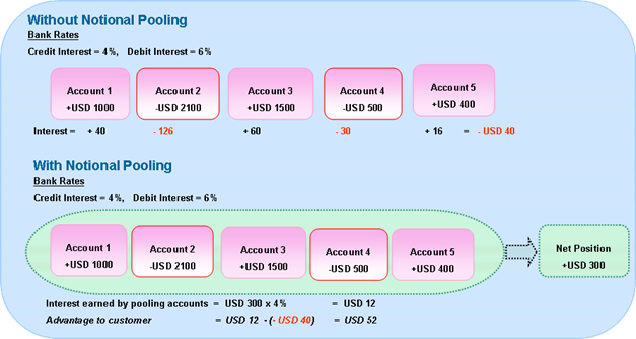
Processes: In most companies, processes grow historically through (international) expansion and M&A activities. The result is a lack of transparency and control of worldwide processes for central finance departments, contributing to a company’s vulnerability to payment fraud. What can you do? If you are evaluating the roll-out of a global ERP-system which includes your finance department, one should think about the current and desired state of (authorization) processes and goals – especially for the finance and treasury department.
Connectivity: Connecting the ERP-system to third party systems is an important factor to consider in terms of payments. Insufficiently secured interfaces with banks, a high number of manual processes as well as the lack of straight-through-processing of payment files increases your risks and have a negative impact on compliance. Moreover, in this context one should not forget the connection with your respective banks. They can be connected through communication channels such as i.e. EBICS, Host2Host, SWIFT, or CAMT. In addition, one has to develop individual formats for each country and bank. Working with our clients around the world, TIS GmbH has achieved savings of between 200.000€ and 1 million € p.a. by implementing its flexible and scalable cloud solution to connect its customers’ banks. This is possible, as TIS owns the most comprehensive library of formats and bank connectors worldwide. This library is accessible to all its clients free of charge, so that you can focus on scaling your worldwide operations.

Change management: In order to ensure a smooth roll-out of your i.e. SAP S4-HANA ERP-system, you should embark on the journey together with your employees. Inform all involved stakeholders early and frequently about the progress of the project. Additionally, you might want to evaluate during the business blueprint phase whether it is advisable to include a specialized consultant. This will increase your chances of success dramatically and support the team spirit.
What are your experiences with IT-projects? I am looking forward to reading your comments.

Christian van Ledden
Sales Executive at Treasury Intelligence Solutions GmbH (TIS)
For additional information please visit the TIS company page on treasuryXL.






 There are lots of discussions concerning risk, but let us start by trying to define what we mean by risk. In today’s article I will focus on liquidity risk. Many companies have very significant credit needs and this needs to be formally addressed with a credit analysis procedure in place. In my former articles I dealt with
There are lots of discussions concerning risk, but let us start by trying to define what we mean by risk. In today’s article I will focus on liquidity risk. Many companies have very significant credit needs and this needs to be formally addressed with a credit analysis procedure in place. In my former articles I dealt with