| 30-12-2016 | Carlo de Meijer |
 In the past three weeks I travelled throughout South Africa. My main focus was on the country, the people, the safaris, the Big Five and not on blockchain! Now being back home I was curious to learn if there were developments in the blockchain area.
In the past three weeks I travelled throughout South Africa. My main focus was on the country, the people, the safaris, the Big Five and not on blockchain! Now being back home I was curious to learn if there were developments in the blockchain area.
A number of interesting reports were launched, amongst others by Euroclear and Deloitte. And there has been growing blockchain and distributed ledger activity in the financial industry from start-ups, to banks, central banks, the market infrastructure and consortia. But also from advisory companies, central government bodies and others.
In my first article on treasuryXL, earlier this week, I wrote about two reports and startups. I want to focus on banks and consortia in this second article about blockchain developments.
BANKS
BNP Paribas completed its first blockchain-based live cross border B2B payments
BNP Paribas has completed its first live cross-border B2B payments between corporate clients using blockchain technology. The transactions, conducted on behalf of packaging outfit Amcor and trading cards group Panini, were cleared in various currencies between BNP Paribas bank accounts located in Germany, the Netherlands and the United Kingdom. For the ‘cash-without borders’ project, the payments were fully processed and cleared in a few minutes. This highlights the potential of the technology to eliminate delays, unexpected fees and processing errors, and pave the way for real time cash management. The bank has strong commitment to follow closely and further accelerate their participation in a number of market initiatives aiming at improving the corporate payments experience using blockchain technology.
Citi backs blockchain startup
Citi has invested in blockchain venture Cobalt DLT, ahead of what the company expects will be a second round of funding in 2017. Cobalt DLT is a blockchain startup aiming to bring distributed ledger technology to the processing of foreign exchange trades. Transactions in the FX market are notoriously inefficient and costly. Currently, foreign exchange trades need multiple records for buyer, seller, broker, clearer and third parties and then reconciliation across multiple systems. Cobalt is now building a post-trade processing network based on distributed ledger technology. The Cobalt DL solution has the potential to significantly improve post-trade services by cutting costs and reducing risk for our industry. Cobalt DL’s FX solution is set to launch in 2017, with 15 institutional participants committed to using the service.
CONSORTIA
While the number of consortia in the blockchain arena are further growing, the bank-backed R3CEV sees some cracks in the consortium. Some of its biggest founding members parted ways. Big names like Goldman Sachs and Banco Santander are leaving the R3CEV consortium. And new reports are surfacing suggesting that others such as JP Morgan, Morgan Stanley, Macquiries, US Bancorp and National Australia Bank may follow soon.
The R3 consortium has its first Spanish-speaking Latam member
But there is also some good news. Creditcorp, a Spanish-speaking Latin American financial institution, has joined the R3 consortium to design and apply distributed and shared ledger-inspired technologies to global financial markets. The bank provides corporate and personal banking, brokerage services, and other financial services across its six principal subsidiaries in Peru, as well as other South American countries including Bolivia, Columbia and Chile, and is listed on the Lima and New York stock exchanges.
R3 and Calypso to develop blockchain trade confirmation system
Blockchain consortium R3 continues to press ahead with new initiatives, partnering with Calypso Technology to develop a multi-party trade confirmation system running on its Corda distributed ledger-based smart contract platform. Calypso will be the first application partner to adopt the R3 platform, utilising the technology to enable counterparties to see all trade tickets on the distributed ledger so they can be sure they are matching against the correct trade.
JPX to form Japanese blockchain consortium
Japan Exchange Group (JPX) is to form a consortium of financial institutions to run trials of the use of blockchain technology in capital markets infrastructures. The exchange will seek participation from a wide range of Japanese financial institutions in order to gather broad industrial expertise ahead of testing in spring 2017. They will consider a structure for efficient information sharing between the DLT engineer community and financial institutions through efforts such as training on DLT technology. The Tokyo Stock Exchange together with the Osaka Exchange and Japan Securities Clearing Corporation (JSCC) will lead the coalition which intends to create a test environment for Proof of Concept (PoC) using Hyperledger fabric, the open source DLT platform, in cooperation with IBM.
Blockchain applications, consortium for Malta Stock Exchange
Malta Stock Exchange (MSE) has announced plans to research and develop into the blockchain technology, and to establish its own consortium. MSE’s committee will be run by MSE board members, blockchain experts and its chairman. The consortium will be sharing knowledge and establishing connections or joint-ventures with each other to assist fintech companies based on the blockchain technology, to grow by supporting them in designing and implementing blockchain applications. Furthermore, with this consortium, the Malta Stock Exchange could be planning its first blockchain application. It is very likely their first application on blockchain will replace standard stock exchange platforms.
South Korea rolls out blockchain consortium
The Korea Financial Investment Association (FIA), along with 21 financial investments and five blockchain companies, have teamed up to form a blockchain consortium. The group has signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) to collaborate on projects and share their expertise on blockchain technology. Moreover, the group aims to create business opportunities for the consortium as well as establishing a platform with the member companies. Its future research projects include the establishment of a common platform for personal authentication due in 2017, researching into clearing and settlement automation in 2018 and 2019, and a platform for over-the-counter trading for 2020.
Microsoft creates Asia’s first blockchain consortium on Azure
Microsoft has teamed up with AMIS and the Industrial Technology Research Institute of Taiwan (ITRI) to form Asia’s first and the most advanced consortium blockchain network on Azure. The consortium includes members such us: Ubon Financial, Cathay Financial Holdings, MegaBank, KGI, Taishin, and CTBC Bank. Aim is to further develop blockchain opportunities in the Taiwan financial market.
The pilot blockchain project is developed using ITRI’s technology (to create an internal application program interface (API)) and Microsoft Azure. AMIS chose Ethereum, to develop a permissioned blockchain, an infrastructure specific to the needs of Taiwan’s financial market. As part of the project, ITRI provided its advanced technology to create an internal application program interface (API), while Azure provided high-speed cloud computing to ensure high security and efficiency for the blockchain infrastructure.
XBRL and ConsenSys work on deploying blockchain tokenization standards
XBRL US, a US non-profit consortium for business reporting standard, has teamed up with Consensys, a blockchain technology company, to work on deploying blockchain tokenization standards. The working group aims to establish a standardized method to represent a token across all blockchain networks in order to eliminate transactional friction and reduce processing costs; enable automation and provenance tracking; and allow interoperability of transactions on a global scale.
The working group will establish goals and action steps by early 2017, and is requesting participation from individuals representing technology, finance, and accounting to provide their expertise in developing tokenization standards that can be used worldwide, for all asset classes.
Source: LinkedIN/Carlo de Meijer

Carlo de Meijer
Economist and researcher

 [email protected]
[email protected]
 With globalisation and an increasingly complex business environment, having an efficient and centralised payment system is vital to any multinational’s success. Recognising this, we at HSBC are proud to have successfully connected to Treasury Intelligence Solutions (TIS) in Asia for automated payment and bank statement processing.
With globalisation and an increasingly complex business environment, having an efficient and centralised payment system is vital to any multinational’s success. Recognising this, we at HSBC are proud to have successfully connected to Treasury Intelligence Solutions (TIS) in Asia for automated payment and bank statement processing.

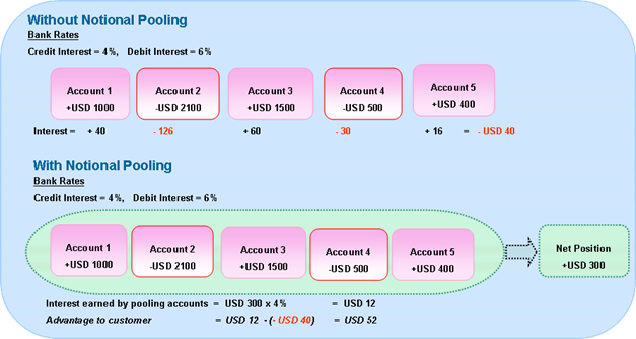
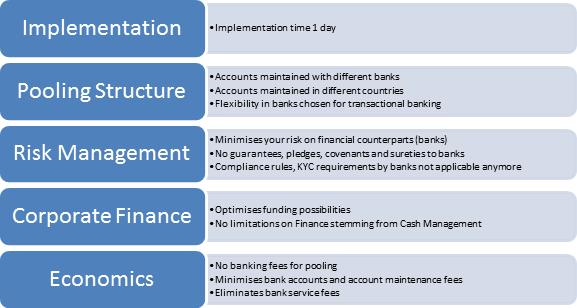

 In december 2016 I travelled throughout South Africa. My main focus was on the country, the people, the safaris, the Big Five and not on blockchain! Being back home I was curious to learn if there were developments in the blockchain area. A number of interesting reports were launched and there had been growing blockchain and distributed ledger activity in the financial industry from start-ups, to banks, central banks, the market infrastructure and consortia.
In december 2016 I travelled throughout South Africa. My main focus was on the country, the people, the safaris, the Big Five and not on blockchain! Being back home I was curious to learn if there were developments in the blockchain area. A number of interesting reports were launched and there had been growing blockchain and distributed ledger activity in the financial industry from start-ups, to banks, central banks, the market infrastructure and consortia. 

 Last November The European Payments Council (EPC) launched the single euro payments area (SEPA) instant credit transfer (SCT Inst) scheme. The scheme will be live in November 2017 and allows the European banks to propose innovative, digital, and fast payment solutions to their customers. The EPC describes the SCT Inst scheme as “a world first, enabling individuals, businesses, corporates and administrations to make instant euro credit transfers between accounts across an international area that will progressively span over 34 European countries. This new scheme is a revolution for the traditional 9 to 5/ weekdays only operating banks. Will it also block the way to relative newcomers like Paypal? Will the banks seize this opportunity and strike back?
Last November The European Payments Council (EPC) launched the single euro payments area (SEPA) instant credit transfer (SCT Inst) scheme. The scheme will be live in November 2017 and allows the European banks to propose innovative, digital, and fast payment solutions to their customers. The EPC describes the SCT Inst scheme as “a world first, enabling individuals, businesses, corporates and administrations to make instant euro credit transfers between accounts across an international area that will progressively span over 34 European countries. This new scheme is a revolution for the traditional 9 to 5/ weekdays only operating banks. Will it also block the way to relative newcomers like Paypal? Will the banks seize this opportunity and strike back?

 Maarten Verheul – Treasury Consultant
Maarten Verheul – Treasury Consultant Er staat op dit moment veel in het nieuws over rentederivaten en de ontwikkelingen rond deze producten. Rentederivaten kunnen nuttig zijn om het renterisico af te dekken, het zijn echter ingewikkelde producten. Als treasurer zult u de werking en de risico’s van het product goed begrijpen. Als u toch behoefte heeft aan voorlichting kunt u zich laten informeren door uw bank. Daarnaast kunt u kennis over de werking van deze producten in huis halen, bijvoorbeeld bij een advieskantoor dat zich specialiseert op het gebied van rentederivaten.
Er staat op dit moment veel in het nieuws over rentederivaten en de ontwikkelingen rond deze producten. Rentederivaten kunnen nuttig zijn om het renterisico af te dekken, het zijn echter ingewikkelde producten. Als treasurer zult u de werking en de risico’s van het product goed begrijpen. Als u toch behoefte heeft aan voorlichting kunt u zich laten informeren door uw bank. Daarnaast kunt u kennis over de werking van deze producten in huis halen, bijvoorbeeld bij een advieskantoor dat zich specialiseert op het gebied van rentederivaten. 
 We came across an interesting ‘panorama’ from McKinsey& Company about the key Fintech trends and asked our expert Hans de Vries to comment on it. He came back with interesting insight, that we want to share with you:
We came across an interesting ‘panorama’ from McKinsey& Company about the key Fintech trends and asked our expert Hans de Vries to comment on it. He came back with interesting insight, that we want to share with you: