Netting: a viable value driver
| 17-12-2018 | BELLIN | treasuryXL |
How to save money and resources with a smart intercompany reconciliation process
The last two decades have seen treasurers graduate from haphazard data collectors to deliberate decision makers. As their empowerment is inextricably linked to the triumph of the internet and the technology it affords, it comes as no surprise that most of them are curious about new developments and eager to partake in them. Yet, the convenience and value of automated intercompany reconciliation is still comparatively underappreciated and overlooked. According to an article published in Financial Management just a few years ago, the vast majority of US companies still reconcile their balance sheet accounts manually and forfeit the countless benefits yielded by a centralized, agreement-driven netting process enabled by today’s technology.
What is Netting?
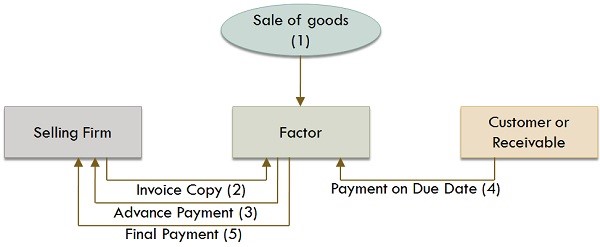
At its most basic level, netting is the offsetting of payables against receivables between two or more group companies to reduce the amount of net payments and save transaction costs. Originally a mere accounting task – ensuring that the balances of two accounts were matching – intercompany reconciliation has, with the advent of modern technology, transformed into an indispensable cash and FX management tool and thus become an integral part of treasury management.
The netting center — technology with teething troubles
The proverbial missing link to an enhanced netting process was the emergence of cloud-based Treasury Management Systems that afford users global visibility and control and enable the implementation of group-wide process automation. Bilateral netting was replaced by multilateral netting (figure 1) via the introduction of netting centers run by the group treasury. Isolated matching between single subsidiaries became obsolete, as the netting center acts as a reconciliation hub across the entire company: payables are made out by the respective group companies to the netting center, receivables get paid to the eligible subsidiaries by the netting center. Classically, this process was either payable- or receivable-driven. On the surface, this seems simple and efficient, but it’s not: as there is no room for doubt or dispute, it is susceptible to errors and abuse. In the case of payments-driven netting, subsidiaries can compromise the system by accidentally or willfully failing to enter invoices, while in a netting process based on receivables, group companies can enter fictitious agreements to garner illegitimate payments. In a setup like this, the netting center is as effective as it is blind – with guillotine-like precision it carries out what the subsidiaries have entered, without verifying its legitimacy. This creates uncertainty among the group companies and fosters catacombs of shadow bookkeeping at the expense of much-needed visibility.
Netting – it’s all about engagement
Therefore, modern multilateral netting systems should not only perform AP/AR matching but are also dispute management systems, performing – as we call it — agreement-driven netting. It enables payable- and receivable-driven netting, but in an advanced manner, as it encourages engagement and promotes transparency. Via the TMS, AP and AR line item data gets collected and subsequently matched. Disagreements are dealt with in a structured dispute process, the rulebook of which is defined by the company’s management according to the requirements of the group. Disputes between subsidiaries get reviewed by the netting center, which acts like a referee, applying said rules. The key principle and the main advantage of this approach is the engagement it fosters: each party gets their say, no one can be taken advantage of, all transactions are transparent as everything gets recorded and the proper settlement of balances is ensured.
Multilateral Netting as a cash and FX management instrument
The advantages of such a process are obvious: With fixed dates for netting runs, incoming payments can be predicted precisely. The netting center respectively the central treasury enjoys maximum control and visibility of cash movements and can optimize the use of funds within the group. The same holds true for FX hedging: netting enables subsidiaries to transfer the FX risk to the central treasury, where seasoned experts deal with it for the entire group. Consequently, the number of FX trades – and with it the transfer and bank fees – gets significantly reduced, as each subsidiary will only have one cashflow per netting run towards or from the netting center in a fixed currency set beforehand. As the netting center acts as an in-house bank, the group companies don’t make any payments via bank accounts anymore, which saves cost and resources and provides added transparency.
Cost reduction via best practice netting: figures!
Let me provide you with just one example from the plethora of companies, who were able to streamline their operations and encounter significant savings via a TMS-based netting process: the Austrian tool manufacturer Tyrolit, whose Success Story and accompanying video we’ve featured previously as part of our We Love Treasury 2 series. Upon counting all payments via bank accounts between group companies, Tyrolit arrived at the impressive number of 600 per month, most of them international, entailing substantial bank fees as well as float. The fact that many of those transactions were made in foreign currency added significant translation costs to that, which were hard to calculate due to the different margins the banks offered. With the roll-out of an agreement-driven netting process across the group, Tyrolit managed to reduce the number of transactions to a mere 5% of the original amount and ended up saving the whopping sum of about 500,000€ per year on bank fees and translation costs alone.
Netting company-wide: benefits, benefits, benefits
By transforming a company’s entire intra-firm trade, a robust multilateral netting process offers benefits galore, including but not limited to:
- a company culture that enables dialogue, promotes engagement and fosters transparency and trust
- facilitated cash and liquidity management via centralized IC reconciliation on fixed dates in fixed currencies
- fair distribution and optimization of refinancing cost
- centralized FX hedging aiding the consolidation of an over-complex banking landscape, reducing bank fees and minimizing translation costs
- overall enhanced efficiency, visibility, security and compliance
By the way: the implementation of netting software is fairly straightforward, software-wise, once you’ve decided that you want to follow through with the process. It’s a one-time technical impact, user-training can be performed very efficiently and hosting as well as outsourcing options are available to overcome capacity shortages. So what are you waiting for?

Dr. Teut Deese
Staff Writer – BELLIN
[button url=”https://www.treasuryxl.com/community/companies/bellin/” text=”View company profile” size=”small” type=”primary” icon=”” external=”1″]
[separator type=”” size=”” icon=””]
Check out the video: “Netting: How to save resources with smart IC Reconciliation,” in which Martin Bellin gives us an in-depth breakdown of how your company can take full advantage of the associated benefits.