| 01-02-2018 | François de Witte |
The main objectives of the cash & liquidity management are to:
- Have the cash funds available to meet all known and unknown commitments
- In the right currency
- In the right place
- At the right time
- Optimize the return of the cash and/or minimize the cost of the short term financing
- Minimize external financing by using internal funding
One of the most important techniques to achieve a better utilization of the available cash is the “cash pooling” or, in other words, the concentration of the cash to make it centrally available. The commonly used techniques in the market are the following:
- Manual cash concentration: Intercompany payments
- Automated Cash Concentration: requires physical movement of funds
- Notional Pooling: without movement of funds
In the present article, we will outline the current types of cash management tools, their advantages and the attention points.
Manual cash concentration: Intercompany payments
For companies, who have only a limited number of accounts to overview, it is recommended to set up a manual cash pooling. In this case, the treasurer overviews daily or weekly the balances of the different accounts, and when there are important debit or credit positions, he will initiate manual payments to balance the positions, and or to concentrate them on the central treasury account. If during the day, important movements take place, the treasurer can make some additional intra-company payments to balance the debit and credit positions. In order to avoid float, it is recommended to use the urgent payments clearing.
The main advantages of the manual cash balancing are the following:
- The easy set up
- The possibility take into account the cash forecasting
- You do not always make daily movements, which facilitates the intercompany loan administration.
However there are some drawbacks / attention points:
- There is a daily / weekly need to make manual interventions. However some treasury software packages provide a solution to automate this process (bank independent cash pooling)
- The banks take additional charges for use of the urgent payments clearing, except if the payments are processed within the same bank
- The overdraft credit lines of the participants are qualified as full lending limits, and hence for the banks there is a higher capital weighting
- When different legal entities are involved, you create a lending /borrowing relationship between the participants. Hence there are legal and tax issues:
- You need to foresee a intra-group lending agreement
- There are possibly withholding tax, transfer pricing and thin capitalization issues
- Within your group, you need to manager the intercompany loan administration.
Automated cash concentration
The automated cash concentration, also called cash balancing, is a pooling technique requiring a physical transfer of funds to or from the participating accounts to concentrator account. The pooling movements are operated automatically by the bank
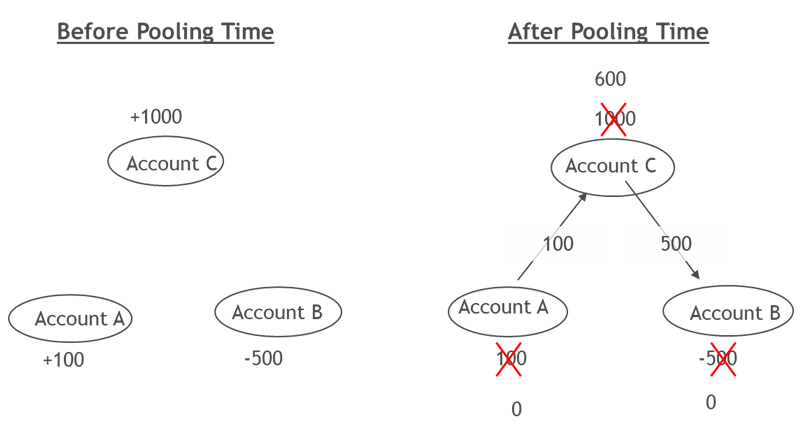
The most commonly used cash concentration is the zero balance cash balancing, as illustrated in the drawing down below. In this solution, the balances of the participants are daily or weekly swept to a concentrating account.
Figure 1: Outline of the zero balance cash balancing
 There are also other forms of cash concentration:
There are also other forms of cash concentration:
- Target cash balancing, to keep a specific amount in each account
- Threshold cash balancing, to move funds only when an account moves in excess of a figure
- Trigger cash balancing, whereby the movements are only initiated if the balance of an account (debit or credit) exceeds a certain amount
- End-of-day or intraday cash balancing
- Domestic or cross-border cash balancing.
There are several advantages to this system, such as:
- There are no manual interventions, as the system is automated
- Several features are possible (multi-layer, domestic and cross-border, target balancing, …)
- There exist a possibility to integrate accounts from third banks
- The system discipline to participants
- With several banks, the intra-day lines, and the intra-day debit positions do not require a capital weighting.
However there are also drawbacks / attention points:
- For value-based cash balancing, there can occur reconciliation issues with ERP systems or treasury management systems, as they usually work on accounting balances
- The cash balancing works only within the same currency. When you manage different currencies, different physical cash balancing structures need to be set up for each currency
- When different legal entities are involved, you create a lending /borrowing relationship between the participants – see also point 2 hereabove
- The automated cash balancing can only work within the same currency (mono-currency).
Notional cash pooling
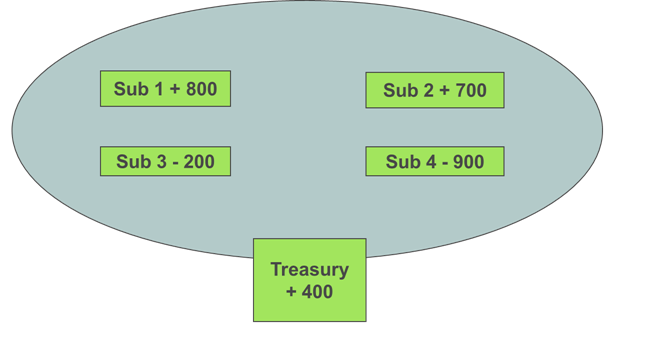
The Notional cash Pooling is a cash pooling where there is no movement of funds. In such a pooling the credit balances of the participants are offset against debit balances of the participants. Hence the net balance of the group is used to calculate the debit or credit interest paid or received.
The system has a flat structure, which means that all the participating Accounts are basically equal to each other. However usually corporates designate one account as the treasury Account, which is then used to manage the system.
Figure 2: Outline of the notional cash pooling
The main advantages of the notional pooling are the following:
- The notional pooling does not require to move funds, and hence:
- No intercompany loan administration
- Less legal and tax issues
- In some jurisdictions (e.g. the UK and NL) the notional pooling can, under certain conditions improve the balance sheet by offsetting surplus balances against group debt
- The notional pooling can include different currencies.
However there are also attention points:
- The full legal offset of debit and credit positions of different legal entities is an issue in several countries
- In some countries notional pooling is not allowed
- Basel III does not always allow that liquidity ratios are calculated by means of netting the outstanding balances of accounts in the notional pool. This means that banks must calculate their ratios based on the gross balances of the individual accounts. Hence they will also look to translate this cost in the pricing of the notional cash pooling.
Legal and tax aspects of cash pooling
Setting up a pooling requires some preparation, and some legal and tax issues need to be addressed, such as:
- Is automated cash pooling (cash balancing or notional) authorized ?
- For cash balancing with different entities
- Transfer pricing issues – Arm’s length rule
- Is debit interest an allowable deduction?
- Withholding tax issues
- Is thin capitalization an issue?
When setting up such structures, in particular when different countries are involved, you need to foresee a due diligence with legal/tax advisors and banks
For cash balancing with different legal entities, a requirement is also to be able to manage intercompany loan administration. There are banks and providers who come up with solutions in this area.

François de Witte
Founder & Senior Consultant at FDW Consult and Senior Expert – Product, Business development and sales manager at Isabel Group





 Met het huidige nieuws rond beursgangen (IPOs = initial public offering) heb ik gezocht op het steekwoord beursgang op treasuryXL en vond geen resultaten. Wellicht omdat de treasury beroepsgroep communiceert in het Engels. Voor Non-Treasurers ga ik bij deze kort in op de basisbeginselen van een beursgang en waarom hier zoveel aandacht voor bestaat.
Met het huidige nieuws rond beursgangen (IPOs = initial public offering) heb ik gezocht op het steekwoord beursgang op treasuryXL en vond geen resultaten. Wellicht omdat de treasury beroepsgroep communiceert in het Engels. Voor Non-Treasurers ga ik bij deze kort in op de basisbeginselen van een beursgang en waarom hier zoveel aandacht voor bestaat.

 There are also other forms of cash concentration:
There are also other forms of cash concentration:


