Exclusive interview with FX specialist Arnoud Doornbos about FX Risk Management
6-1-2020 | by Kendra Keydeniers | Arnoud Doornbos | Ilfa Group
On January 23rd, 2020 Ilfa and Global Reach are organising a masterclass on foreign exchange risk management. FX experts Michael Jansen of Global Reach and Arnoud Doornbos of Ilfa will guide you through the design of a FX risk management program and demonstrate which opportunities a program like this has for your organisation.
Go to event and register for the masterclass. Places are limited so we recommend to secure your spot today.
treasuryXL is delighted to share our exclusive interview with one of the organizers and FX specialist, Arnoud Doornbos of Ilfa.
What is Foreign Exchange Risk Management?
Foreign exchange risk management strategy or FX hedging strategy are terms used to define all the measures devised by businesses or investors to protect the value of their cash flows, assets or liabilities from adverse fluctuations of the exchange rate.
Hedging is used by companies to manage their currency exposure. If a company needs to buy or sell one currency for another, they are exposed to fluctuations in the foreign exchange market that could affect their costs (or revenues) and ultimately their profit.
By booking a hedge, companies protect an exchange rate against a specified sum of currency for a desired timescale, providing companies with certainty.
There are a range of products that can be used for hedging, depending on the companies objective and the exposure they are trying to protect.
Typically, a company would hedge their foreign exchange (FX) exposure to protect its profit margin from market volatility. Hedging is most common in companies that have an exposure to a secondary currency and have fixed prices on their products or services.
What are the types of Foreign Exchange risk?
Foreign Exchange exposure is classified into three types:
- Transaction exposure deals with actual foreign currency transaction.
- Translation exposure deals with the accounting representation
- Economic exposure deals with little macro level exposure which may be true for the whole industry rather than just the firm under concern.
Currency risks can have various effects on a company, whether it operates domestically or internationally. Transaction and economic risks affect a company’s cash flows, while transaction risk represents the future and known cash flows. Economic risk represents the future (but unknown) cash flows. Translation risk has no cash flow effect, although it could be transformed into transaction risk or economic risk if the company were to realize the value of its foreign currency assets or liabilities. Risk can be tricky to understand, but by breaking it up into these categories, it is easier to see how that risk affects a company’s balance sheet.
What are the most common critical Foreign Exchange risk problems that companies make?
Businesses that operate internationally or domestically must deal with various risks when trading in currencies other than their home currency.
Companies typically generate capital by borrowing debt or issuing equity and then use this to invest in assets and try to generate a return on the investment. The investment might be in assets overseas and financed in foreign currencies, or the company’s products might be sold to customers overseas who pay in their local currencies.
Domestic companies that sell only to domestic customers might still face currency risk because the raw materials they buy are priced in a foreign currency. Companies that do business in just their home currency can still face currency risk if their competitors operate in a different home currency.
What critical elements of Foreign Exchange risk are often overlooked?
One of the critical elements of the currency risk that are overlooked is the correct identification of the type of FX risk. A distinction must be made between certain and uncertain cash flows in FX. With certain cash flows, the company has to deal with a linear risk that must be covered with a linear financial hedging instrument, an FX forward. With an uncertain cash flow, risk profile is not linear and it is dangerous to use FX Forwards to hedge. FX Options are better financial products to hedge.
If the company does not include FX Options in its Treasury policy, the second best option is to use FX forwards for, for example, 50% of the principal sum of the underlying risk.
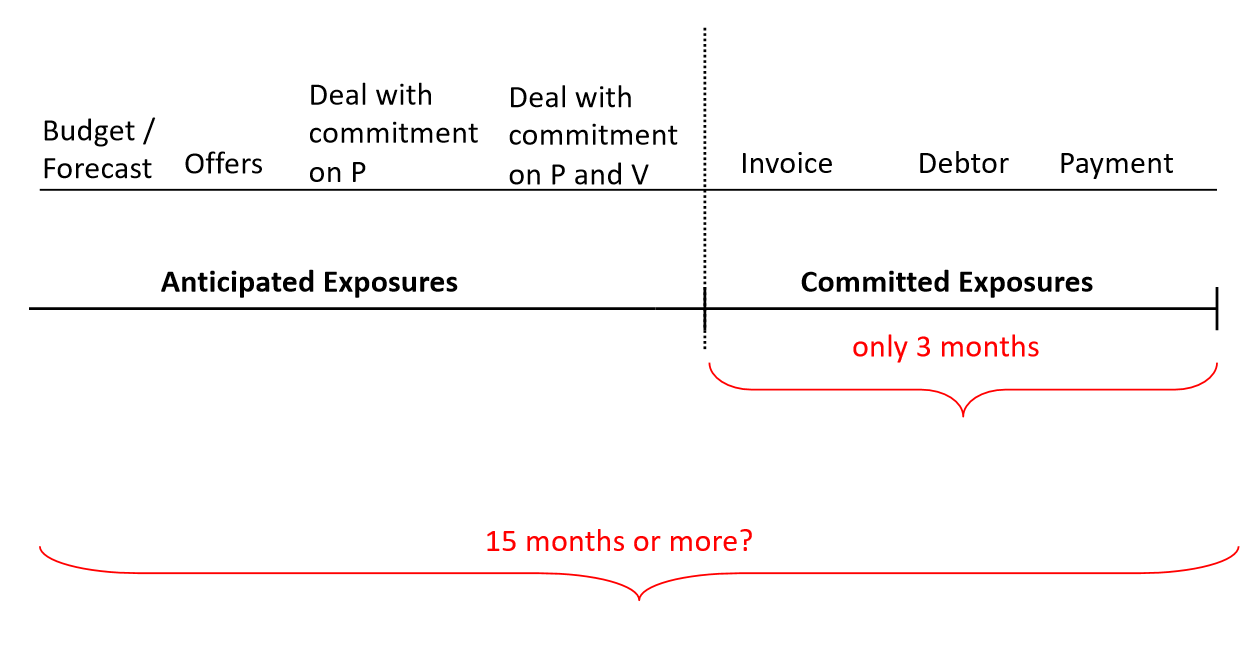
Anticipated and committed exposure cycle
How can you measure Foreign Exchange risk and the different types?
There are many ways to measure foreign exchange risk, ranging from simple to quite complex. Sophisticated measures such as ‘value at risk’ may be mathematically complex and require significant computing power.
Register of foreign currency exposures
A very simple method is to maintain a register of exposures and their associated foreign exchange hedges. Basically the details of each hedge are recorded against its relevant exposure. This type of approach may also assist with compliance with accounting standards.
Table of projected foreign currency cashflows
Where the business both pays and receives foreign currency, it will be necessary to measure the net surplus or deficit for each currency. This can be done by projecting foreign currency cash flows. This not only indicates whether the business has a surplus or is short of a particular currency, but also the timing of currency flows.
To properly determine the FX risk, account must be taken of the differences in sensitivity of the incoming and outgoing FX cash flows.
Sensitivity analysis
A further extension of the previous measure is to undertake sensitivity analysis to measure the potential impact on the business of an adverse movement in exchange rates. This may be done by choosing arbitrary movements in exchange rates or by basing exchange rate movements on past history.
Value at risk
Some businesses, particularly financial institutions, use a probability approach when undertaking sensitivity analysis. This is known as ‘value at risk’. While it is useful to know the potential impact of a given change in exchange rates (say a USD one cent movement) the question will arise: how often does this happen? Accordingly, we can do a sensitivity analysis using past price history and apply it to the current position. Then, given the business’s current position, and based on exchange rates observed over the last two years, it can be 99 per cent confident that it will not lose more than a certain amount, given a certain movement in exchange rates. In effect, the business has used actual rate history to model the potential impact of exchange rate movements on its foreign currency exposures.
What steps do you need to make to create a Foreign Exchange strategy?
Transaction risk is often hedged tactically (selectively) or strategically to preserve cash flows and earnings, depending on the companies treasury view on the future movements of the currencies involved. Tactical hedging is used by most firms to hedge their transaction currency risk relating to short-term receivable and payable transactions, while strategic hedging is used for longer-period transactions.
Translation, or balance sheet, risk is hedged very infrequently and non-systematically, often to avoid the impact of possible abrupt currency shocks on net assets. This risk involves mainly long-term foreign exposures, such as the firm’s valuation of subsidiaries, its debt structure and international investments. However, the long-term nature of these items and the fact that currency translation affects the balance sheet rather than the income statement of a company, make hedging of the translation risk less of a priority for management. For the translation of currency risk of a subsidiary’s value, it is standard practice to hedge the net balance sheet exposures, i.e., the net assets (gross assets less liabilities) of the subsidiary that might be affected by an adverse exchange rate move.
Translation risk is for a large part a Finance issue. Within the framework of hedging the exchange rate risk in a consolidated balance sheet, the issue of hedging a companies debt profile is also of paramount importance. The currency and maturity composition of a firm’s debt determines the susceptibility of its net equity and earnings to exchange rate changes. To reduce the impact of exchange rates on the volatility of earnings, the company may use an optimization model to devise an optimal set of hedging strategies to manage its currency risk.
What is, in your perception, the biggest benefit of a working Foreign Exchange strategy?
Foreign exchange risk management is thus fundamental but it is often considered to be too complex, expensive and time-consuming. Nonetheless, with a simple, tailored monitoring activity, it can neutralise currency fluctuations and bring the following benefits: Securing marketing margins. Optimising cash-flow estimates.
What is your best advise for companies dealing with Foreign Exchange risk?
This Forex market is open 24 hours a day, 5 days a week and with a daily volume of $ 6.6 trillion the most liquid and largest financial market in the world. For most companies, FX risks are non-core risks The objective of most companies is not to be an FX trader. By correctly identifying and quantifying the FX risks and then neutralizing them with the correct financial FX hedging instruments, companies will have little or no trouble with currency fluctuations on the financial FX markets. The implementation of the correct procedures forms the basis of good FX risk management and will make opportunistic behavior of management disappear.
Associate Partner Ilfa
FX specialist