15-06-2022 | treasuryXL | TIS | LinkedIn |
This blog highlights the primary considerations that treasury and IT teams must make when determining whether to build custom in-house bank connectivity and payments solutions or contract the services and software of a specialized 3rd party vendor. After evaluating the main benefits and drawbacks of each option, we provide a list of helpful questions for practitioners to consider as they decide whether building or purchasing a solution best suits their needs.
Source

How Does the “Build vs Buy” Debate Typically Surface Within Organizations?
In today’s remote and digitally operated business environment, it’s no secret that organizations have grown deeply reliant on technology to manage and automate their core treasury and finance functions.
Realistically, a “modern” company operating in 2022 will be doing business through a myriad of banks, accounts, currencies, and entities. They will also likely have hundreds or thousands of vendors, partners, and customers within their network. As a result, digital payments and cashflows are moving in and out of the business constantly, and every movement must be monitored and controlled by treasury teams that often consist of just a few employees.
Because of treasury’s limited personnel bandwidth, any issues with adopting the right bank connectivity and payments stack to automate their core operations almost always lead to excess complexity and manual strain. It can also result in significant security and compliance gaps, along with general inefficiency across crucial processes like transaction processing, liquidity management, balance reporting, and cash forecasting.
But while most treasury and IT groups today can agree that developing a robust connectivity and payments stack is critically important, each internal stakeholder will likely have their own idea regarding what the “best-fit” version of this technology stack actually looks like.
Why is this?
As companies grow over time, the systems they use to manage payments and connect with their banks must evolve accordingly. Because managing a few bank accounts and transactions in a single country and currency is a fundamentally different task compared to managing dozens of banks, hundreds of accounts, and thousands of payments across numerous countries and currencies, companies cannot rely on the same solutions and structure they’ve always used to sustain them as they scale.
Instead, in order to maintain compatibility with new payment formats and channels like ISO 20022 and SWIFT GPI, connect with regional payment networks like NACHA and EBICS, or accommodate custom bank connectivity protocols (Host-2-Host / SFTP, APIs, etc.), growing enterprises will inevitably reach a point where their existing payments and banking architecture must undergo a significant overhaul.
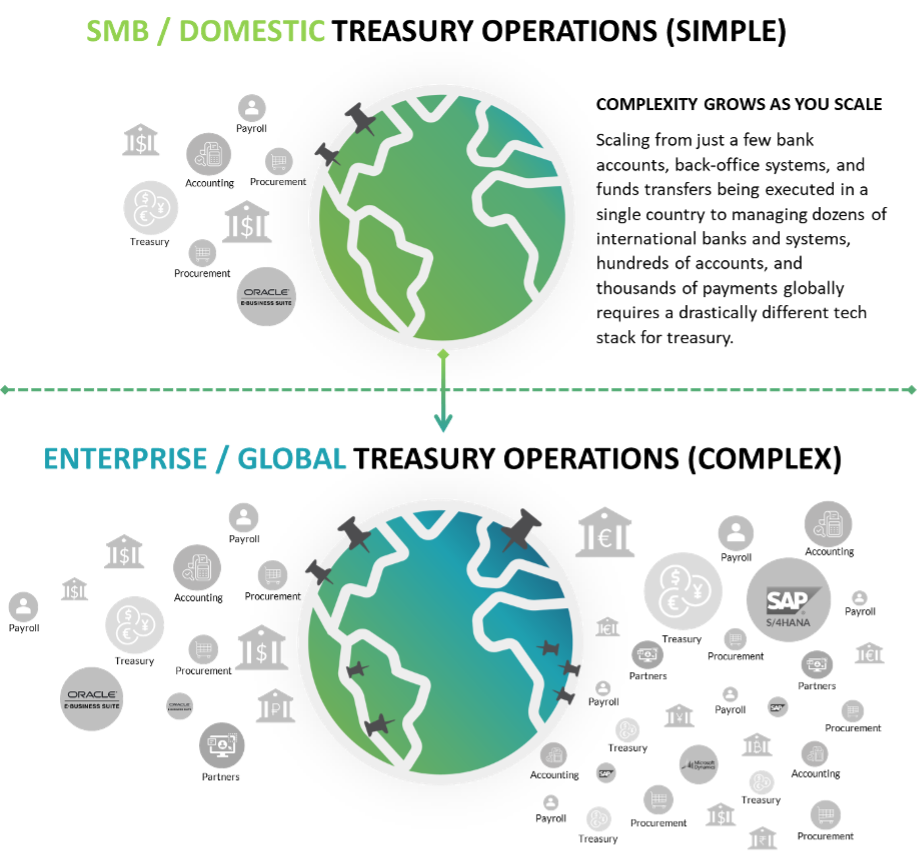
However, as this evolution occurs and internal stakeholders recognize the need to upgrade their connectivity architecture, disagreements often arise over which vendor or “type” of solution is the best fit. Given that there are hundreds of available 3rd party solutions that could potentially address treasury’s requirements, as well as a variety of internally developed applications that could be created and deployed by IT teams, it is common for different stakeholders to have contrasting views over which option is the smartest choice.
This is where the “Build vs Buy” technology argument most frequently comes into play.
Understanding Both Sides of the Build vs Buy Argument
As organizations recognize the need to upgrade their payments and connectivity capabilities, there are two main approaches they could leverage to address the issue. The first is to use internal IT resources and expertise to build a customized solution for treasury, and the second is to purchase a specialized solution from a 3rd party provider.
But which option is the best choice?
Let’s quickly review the key benefits and drawbacks of each option.
Building an Internal Connectivity Solution
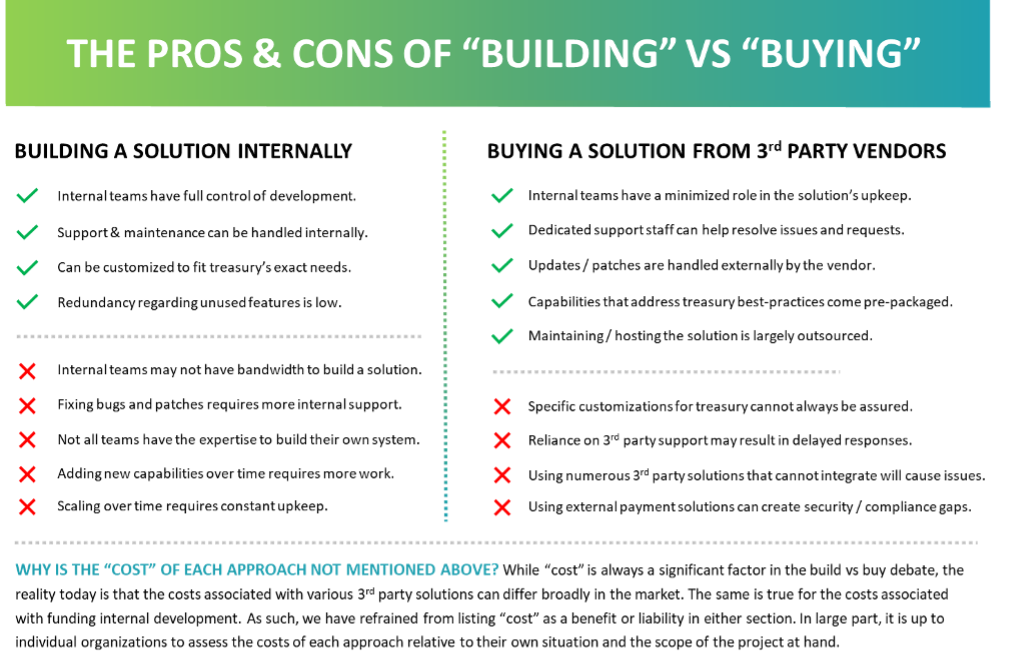
Organizations that prefer to create their own custom connectivity solutions internally using IT resources and expertise will likely have a greater ability to customize the offering in a manner that best addresses all their needs. To date, several prominent ERPs offer modules or plugins that give IT staff the ability to build custom formats and configure their own connectivity protocols. However, this option requires a significant amount of bandwidth and maintenance from treasury and IT teams, as well as a high degree of expertise and technical prowess to support the solution over time. The below pros and cons list highlights this reality in more detail.
PROS
- IT and Treasury teams know firsthand what the main requirements and preferences are.
- Support and maintenance for the solution can be handled internally.
- The solution can be customized to fit the exact needs of the enterprise.
- Complexity and redundancy regarding unnecessary features are kept to a minimum.
CONS
- IT and treasury teams may not have the bandwidth to build their own internal solution.
- Fixing bugs and patches requires internal support, which is not always readily available.
- Not all internal teams have the expertise required to build complex connectivity solutions.
- Supporting the need for new formats and connectivity protocols requires more custom work.
- Scaling over time requires constant upkeep and maintenance from internal resources.
Adopting a 3rd Party Connectivity Solution
Compared to building an internal solution, adopting a 3rd party connectivity and payments solution usually requires less of treasury and IT’s time, and there is less effort required to develop, implement, and maintain the solution. However, there is also the chance that this solution will require the purchase of redundant or unnecessary features. At the same time, improper or incomplete implementation of a 3rd party solution can cause severe integration, security, and compliance issues over time. More about these pros and cons are highlighted below.
PROS
- IT and Treasury teams have a minimized role in the solution’s implementation and upkeep.
- Dedicated customer support staff can help resolve issues and requests.
- Updates and patches are normally handled externally by the vendor.
- Specialist functionality is pre-packaged to address best practices in connectivity and payments.
- Liability on the company to maintain, host, and secure the solution is largely outsourced.
CONS
- Specific customization of the product for treasury teams cannot always be assured.
- Reliance on 3rd party vendors for support and upkeep may result in delayed responses and feedback.
- Tech complexity can quickly escalate if companies start adopting numerous 3rd party solutions to manage various functions, especially if they do not integrate well with one another.
- Using external solutions for data and payments can create additional security risks and compliance issues.
As showcased by the above bullets, a company’s decision to build or buy its payments and connectivity solutions should always depend on its unique circumstances. For instance, a company with sufficient IT personnel and internal expertise might have the bandwidth to create and maintain a solution on its own. However, if treasury and IT teams are already exasperated with their current list of responsibilities and don’t have the time or expertise necessary to create and maintain their own solution, it probably makes more sense to begin evaluating the services of a 3rd party provider.
For treasury teams who are presently evaluating their options and need help deciding on the best course of action, the following considerations will help provide more clarity during the decision-making process.
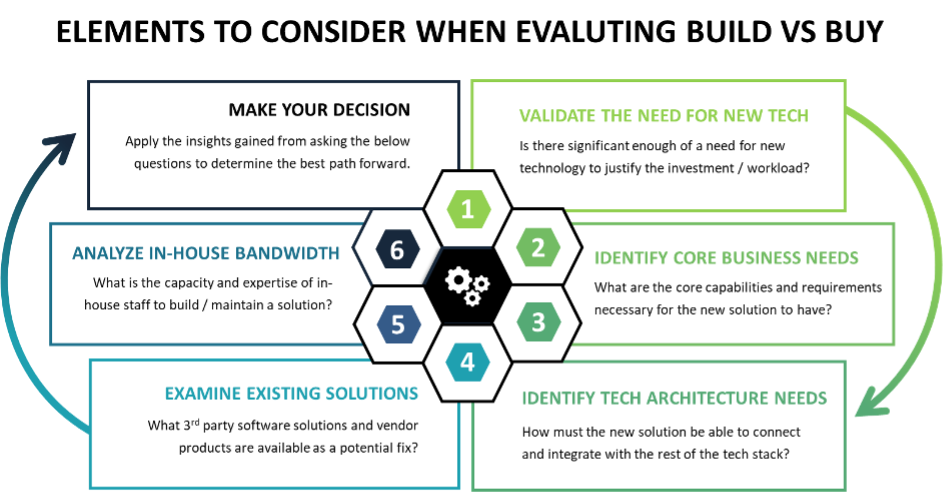
A Checklist to Walk Through When Deciding to Build or Buy Your Next Connectivity Solution
1. Validate the Need for New Technology
Many organizations have their eye on new technology before identifying any legitimate business need. Sometimes this “cart before the horse” approach is due to rigid business processes, lack of technical knowledge, or pure product hype. Decision-makers are very often awed by product suite success stories, dynamite product demonstrations, and industry analysts’ evaluation of technology—even when they haven’t formally identified a need for the technology.
To avoid these pitfalls, treasury and IT teams need to first validate the need for upgraded connectivity and payment protocols, prior to even beginning to evaluate which solution makes the most sense.
Last, but not least, tech leaders need to provide an estimated return on investment (ROI) for any new solution, along with a description of how ROI will be measured. It is surprising how many programs are initiated without considering ROI or added business value upfront. Many of these projects consume a lot of budget and time before leaders realize that either the solution will not add value or there is not a legitimate business need.
2. Identify Core Connectivity & Payment Requirements
In large organizations, pinpointing core connectivity requirements is often easier said than done. Still, it is a critically important step to take before deciding to implement a new solution. A core business requirement is one that must be supported by the solution to continue functioning as intended. For multinational organizations, core connectivity requirements may involve compatibility with numerous format types (EDI, BAI, SWIFT MT, ISO 20022, etc.) as well as numerous bank channels (SWIFT, H2H, EBICS, etc.) and back-office integrations (APIs and plugins for ERPs or TMSs).
Although determining treasury’s exact connectivity requirements may be difficult, it is extremely important to identify these core functional requirements first—not technology or design requirements. This is the only way to ensure unnecessary or redundant functionality is not purchased erroneously, and also ensures that critical requirements are never accidentally overlooked and unaddressed through whatever solution is ultimately chosen.
3. Consider Your Technology Architecture Requirements
Going a step further than the above point, it’s safe to assume that organizations are already using technology to enable other business processes. To reduce the cost and liability of this technology, your organization has also likely adopted standards related to how internal solutions are implemented and maintained.
As such, it is extremely important to identify any architectural requirements or standards that a solution must adhere to before determining if a 3rd party solution or an internal solution is the best choice. Some factors that may restrict the solution choice are as follows:
- Information security strategy, compliance policies, and privacy standards (SOC 1 & 2, GDPR, etc.)
- The state of current / planned systems with which the solution will be interfacing
- What the preferred hosting structure is for the new solution (on-premise, SaaS, etc.)
- Type and complexity of integrations that must be supported by the solution
- Operating systems in use by the organization and their partners/banks/customers/entities
4. Examine & Evaluate Existing Solutions FIRST
At this point, a business need has been pinpointed, ROI has been estimated, and both core business and architectural restrictions have been identified. Leaders should now take a good look at existing systems.
It is not uncommon that different departments or entities of a large, global organization are not aware of what systems exist in other areas of the company. As a result, businesses will often implement multiple versions or forms of the same technology, only to discover that another system within the organization could have supported treasury’s new requirements with little to no modification. Thus, before deciding on the “best-fit” solutions approach, you should determine if any existing system(s) within the organization can be easily scaled or extended to meet your business need.
5. Compare In-House Expertise & Bandwidth Relative to Current AND Future Capabilities Required
One major factor that can significantly reduce the ROI of a custom-built solution (and in many cases, ultimately causes the project to fail) is the lack of available personnel with proper skill sets. In reality, the process of designing and deploying custom connectivity solutions that are both scalable and extensible is a massive undertaking for both treasury and IT. Unless one of your business areas is product development or you have an abundance of available IT support, there is an extremely high probability that your operations and maintenance technology resources will not be able to build, sustain, and support an internal solution, especially as new needs and requirements arise over time.
It is never profitable to let personnel gain these skills and experience by developing business-essential systems. Yet, more often than not, decision-makers see the short-term cost differences between an internally-built vs 3rd party solution and decide to try and build their own in order to save money. However, unless you’re supremely confident in the skillsets and bandwidth of both your treasury and IT teams, this option is not recommended.
Why TIS is the Ideal Provider for Global Payments, Liquidity Management, & Bank Connectivity
Ultimately, any organization evaluating whether to build or buy its next solution will have to closely analyze its own operations in order to make the best decision.
In cases where organizations require support for a complex array of payments and bank connectivity protocols and are open to considering a 3rd party vendor, they should closely evaluate the capabilities provided by TIS.
The cloud-based, fully-supported platform provided by TIS offers a global, multi-channel, and multi-bank connectivity ecosystem that streamlines and automates the processing of a company’s payments across all their global entities and systems. By sitting above an enterprise’s technology stack and connecting with all their back-office, banking, and 3rd party solutions, TIS effectively breaks down department and geographic silos to allow 360-degree visibility and control. To date, the ~200 organizations that have integrated TIS with their global ERPs, TMSs, and banking landscape have achieved near-100% real-time transparency into their payments and liquidity. This has benefitted a broad variety of internal stakeholders and has also enabled them to access information through their platform of choice since the data that passes through TIS is always delivered back to the originating systems.
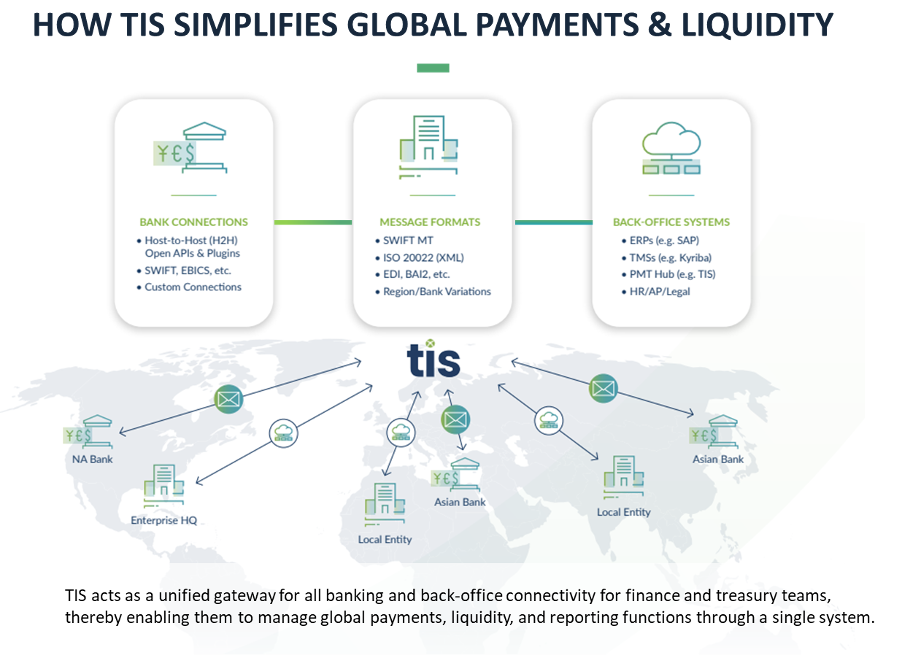
Because of the deep connections that TIS maintains with internal systems such as ERPs or TMSs, external banks, and 3rd party vendors, the process of managing payments is simplified for every internal stakeholder. C-suite executives, treasury, accounting, AP, legal, HR, and other key personnel can access whatever financial data they need, exactly when they need it. And by automating this flow of information for both inbound and outbound payments, TIS provides the control and flexibility that enterprises need to function at their highest level.
Finally, with the global payments data we have amassed and the decades of experience our team has in orchestrating enterprise payments, we are uniquely equipped to help enterprises accurately benchmark their payments performance and provide tailored advice on how to optimize, grow, and mature. Ultimately, this rich data and deep experience are what enable us to continually provide industry-leading payment solutions and support to our enterprise customers.
In the digital world of enterprise payments, TIS is here to help you reimagine and simplify.
For more information about how TIS can help you, visit our website or browse our latest resources!