| 8-8-2017 | Carlo de Meijer |
 Early July SWIFT announced that 22 global banks recently joined its Blockchain proof of concept (PoC) initiative introduced in January this year in collaboration with six leading correspondent banks (ANZ, BNP Paribas, BNY Mellon, RBC Royal Bank and Wells Fargo). The PoC is part of SWIFT’s ‘gpi’ (global payments innovation) service, the new standard for cross-border payments, aimed to “re-arm the correspondent banking system for a new age of technological disruption”.
Early July SWIFT announced that 22 global banks recently joined its Blockchain proof of concept (PoC) initiative introduced in January this year in collaboration with six leading correspondent banks (ANZ, BNP Paribas, BNY Mellon, RBC Royal Bank and Wells Fargo). The PoC is part of SWIFT’s ‘gpi’ (global payments innovation) service, the new standard for cross-border payments, aimed to “re-arm the correspondent banking system for a new age of technological disruption”.
This Blockchain PoC initiative is designed to explore whether blockchain technology can help banks to improve the reconciliation of their international nostro accounts in real-time, optimising their global liquidity. If so, that would be a break through event for both SWIFT and blockchain.
Present state
Currently, banks cannot monitor their account positions in real-time due to lack of intraday reporting coverage. The present pain points banks currently experience when making cross-border payments center around a lack of visibility into the end-to-end transactions lifecycle. Under the current correspondent banking model, banks need to monitor the funds in their overseas accounts via debit and credit updates and end-of-day statements. The maintenance and operational work involved represents a significant portion of the cost of making cross-border payments.
“Cross border payments are like a black box for us. We don’t know when the funds will be credited, we don’t know what fees will be charged and we also have problems with reconciliation”. states Martin Schlageter, head of Treasury Operations at Swiss healthcare conglomerate Roche.
As such, the POC recognises the need for banks to receive real-time liquidity data in order to manage funds throughout the business day.
SWIFT GPI service
The PoC is being undertaken as part of SWIFT gpi, a new service that “may revolutionise the cross-border payments industry by combining real-time payments tracking with the speed and certainty of same-day settlement for international payments”.
The SWIFT gpi should be seen as SWIFT’s response to the problems they faced after a series of attacks events that showed that “all was not as secure as everyone believed”. SWIFT gpi initiative was first announced at the annual Sibos conference in 2015. The project went into live production in January this year to address core problems related to speed, transparency and traceability of cross border payments.
SWIFT gpi not only delivers a much-needed improvement in the speed of transaction, but also improves overall customer experience by creating predictable settlement times and clear statuses, through additional (unaltered transfer of) information on remittances and transparency around the FX rates and fees applied throughout the payment cycle.
“The ability to deliver enhanced remittance information alongside the payment will help customers make better decisions along the payment chain, while also creating better efficiency opportunities. The decision to make gpi available in the “cloud” is also exciting, and we anticipate this will lead to the development of entirely new services, that combine SWIFT gpi with capabilities provided by banks, clients and vendors.“ says Tom Halpin, Global Head of Payments Product Management, HSBC Global Liquidity and Cash Management
Key features
Key features of the SWIFT gpi service include a secure tracking database in the cloud accessible via APIs, and enhanced business rules.
Cornerstone of SWIFT gpi is the highly innovative new cross-border TRACKER, a special tracking feature that enables international payments to be traced real-time. It allows banks to provide corporate treasurers with a real-time, end-to-end view (visibility) on the status of their payments, including confirmations of the amount credited to the beneficiaries’ account. The Tracker is available via an open API, making it compatible with proprietary banking systems worldwide – helping to ensure maximum impact of gpi benefits at a greater adoption speed.
A second key feature is the OBSERVER, a quality assurance tool that monitors participants’ adherence to the gpi business rules. Gpi’s transparency ensures that remittance information such as invoice references, is transferred unaltered to recipients.
Gpi uptake
Membership is open to any supervised financial institution that agrees to comply with SWIFT’s business rules. But also non-bank organisations can join SWIFT gpi initiative. The SWIFT gpi service has received considerable bank support across the globe. And the number of global transaction banks that are actively using SWIFT’s gpi service is continuously growing. Since its launch the number of banks that are live with SWIFT gpi has risen beyond 100, and hundreds of thousands GPI payments have already been sent across 85 country corridors. This represents more than 75% of all SWIFT cross border payments.
“The increasing number of banks going live on this service addresses the demands of corporate treasurers. Hence, banks cannot afford to not join the initiative and go live as soon as possible. Our expectation is that all of our cross-border payments will be end-to-end Swift gpi payments in the future.” Group of Swiss corporates
SWIFT expects that numerous additional banks will join the gpi initiative in the coming months. The ambition is for all countries to be live by the end of 2017.
Phased approach
Next to the design of the second phase of SWIFT gpi, that is already underway focusing on additional digital capabilities and further enhancements such as ‘a rich payment data service’, for its third gpi phase SWIFT started exploring the potential of new technologies such as Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT), including blockchain, through a Proof of Concept (PoC).
SWIFT Blockchain PoC
Launched in January 2017 with six founding banks the SWIFT Blockchain PoC initiative, designed to validate/explore whether blockchain can be used by banks to improve the reconciliation of their international nostro accounts (these are accounts that a bank holds in a foreign currency in another bank to handle international financial transactions for their customers) (these are accounts that a bank holds in a foreign currency in another bank to handle international financial transactions for their customers) in real –time, optimising their global liquidity. At its core, the PoC builds on SWIFT’s rulebook as part of the intraday liquidity standard gpi.
This SWIFT Blockchain PoC initiative aims to help banks overcome significant challenges in monitoring and managing their international nostro accounts, which are crucial to the facilitation of cross border payments.
“Whilst existing DLTs are not currently mature enough for cross-border payments, this technology, bolstered by some additional features from SWIFT, may be interesting for the associated account reconciliation,” “This PoC gives us the opportunity to test DLT and determine if it can be applied to this particular use case.” Wim Raymaekers, Head of Banking Market and SWIFT gpi at SWIFT
Characteristics
In developing the POC, SWIFT is leveraging the Hyperledger Fabric v1.0 technology, and combining it with key SWIFT assets, to bring it in line with the financial industry’s requirements.
“SWIFT will leverage its strong governance, PKI security scheme, BIC legal identifier framework and liquidity standards expertise to deliver a distinctive DLT PoC platform for the benefit of its community.” Damien Vanderveken, Head of R&D, SWIFTLabs and User Experience at SWIFT
The PoC application will use a private permissioned blockchain in a closed user group environment, with specific user profiles and strong data controls. User privileges and data access will be strictly governed. This to ensure that all the information related to nostro/vostro accounts is kept private. Only account owners and its correspondent banking partners will see the details.
Collaboration
SWIFT gpi member banks can apply to participate in this Blockchain PoC. Next to the 6 founding banks, another 22 banks have recently joined the SWIFT blockchain PoC. They include include:
ABN AMRO Bank; ABSA Bank; BBVA; Banco Santander; China Construction Bank; China Minsheng Banking; Commerzbank; Deutsche Bank; Erste Group Bank; FirstRand Bank; Intesa Sanpaolo; JPMorgan Chase; Lloyds Bank; Mashreq Bank; Nedbank; Rabobank; Société Générale; Standard Bank of South Africa; Standard Chartered Bank; Sumitomo Mitsui Banking Corporation; UniCredit; Westpac Banking Corporation.
“Collaboration is the cornerstone of innovation,” “This new group of banks allows us to greatly extend the scope of multi-lateral testing of the blockchain application and thus adds considerable weight to the findings. We warmly welcome the new banks and look forward to their insights” says Wim Raymaekers, head of banking markets and SWIFT gpi at SWIFT.
Process
Moving forward, the SWIFT PoC Blockchain application will undergo testing, with the results scheduled to be published in September and presented at Sibos in Toronto in October. Working independently of the founding banks, the 22 institutions will act as a validation group to test in a deeper way the PoC’s Blockchain application, that is currently under development by SWIFT and the group of six founding banks. They will evaluate how the technology scales and performs.
Benefits
For banks
The potential business benefits ensuing from a successful SWIFT blockchain POC may be significant. If it proves to enable banks reconcile those nostro accounts more efficiently and in real time, that may lower costs and operational risk.
“The potential business benefits ensuing from the PoC are clear,” “If banks could manage their nostro account liquidity in real-time, it would allow them to accurately gauge how much money is required in each account at any given point, ultimately enabling them to free up significant funds for other investments.” Damien Vanderveken, head of R&D, SWIFTLab and UX at SWIFT.
It brings together banks worldwide who want to offer an enhanced cross-border payments experience to their corporate clients. By being part of SWIFT gpi, banks may improve the quality of their correspondent relationships and networks, helping to reduce risks and management costs and improve compliance.
“Transparency is key to a good end-to-end client experience. SWIFT gpi is a significant step in the evolution of correspondent banking, which remains the primary means through which cross-border payments are delivered worldwide. Bank of America Merrill Lynch is pleased to be working with like-minded institutions around the world to better serve each other and our respective customers.” states Greg Murray, head of Global Product Management for High Value Payments and FI/NBFI Products in Global Transaction Services at Bank of America Merrill Lynch.
For corporate treasurers
SWIFT gpi may enable corporates engaged in international trade to get paid for services, or delivery of goods, in a more timely fashion, enabling a faster supply chain process. It also enables a more accurate reconciliation of payments and invoices, optimizes liquidity with improved cash forecasts and reduces exposure to FX risks with same-day processing of funds in the beneficiary’s time zone.
“Being part of SWIFT gpi, and working with our industry counterparts, is giving correspondent banks a platform to examine and refine current processes, and to collaborate and explore different, more efficient ways of doing things. Ultimately, our clients will benefit most from this initiative,” Kent Marais, head of TPS product management at Standard Bank SA.
SWIFT and the banks have designed the gpi services so that banks have flexibility in how they offer the new services. They can deliver the gpi service in very different ways. Services could potentially include enhanced invoice presentment and reconciliation to facilitate financial supply chains, exchange of supply chain documentation to improve global trade, exchange and interactive enquiry of account and processing conditions to improve end-to-end straight through processing, and providing additional party and transaction information to support compliance and sanctions screening of cross-border payments.
Enhanced cross-border payment service
“SWIFT has addressed several of the pain points corporates have had with cross-border payments,” “Changes to existing corporate payments infrastructures should be very limited, if any. So hopefully, corporates won’t need to make any major investments to benefit from smoother cross-border payments.” says Magnus Carlsson, AFP’s manager of treasury and payments
Given the size of the number of banks and corporates participating in SWIFT gpi, the SWIFT Blockchain PoC may face the challenge of scalability. If that could be solved in a successful way it may be another prove of the viability of blockchain and DLT to enhance cross-border payments.

Carlo de Meijer
Economist and researcher
More on blockchain from this author:
Blockchain: accelerated activity in trade finance
Blockchain and derivatives: Re-imagining the industry
The digital trade chain: The blockchain train is rolling
Please feel free to visit the treasuryXL/articles page to see more articles.



 PSD2 is a recurring topic which is of great concern to financial institutions and other payment service providers, as well as finance professionals at corporates all over the world. We read an interesting article about the disruption and innovation of open banking at
PSD2 is a recurring topic which is of great concern to financial institutions and other payment service providers, as well as finance professionals at corporates all over the world. We read an interesting article about the disruption and innovation of open banking at  Early July SWIFT announced that 22 global banks recently joined its Blockchain proof of concept (PoC) initiative introduced in January this year in collaboration with six leading correspondent banks (ANZ, BNP Paribas, BNY Mellon, RBC Royal Bank and Wells Fargo). The PoC is part of SWIFT’s ‘gpi’ (global payments innovation) service, the new standard for cross-border payments, aimed to “re-arm the correspondent banking system for a new age of technological disruption”.
Early July SWIFT announced that 22 global banks recently joined its Blockchain proof of concept (PoC) initiative introduced in January this year in collaboration with six leading correspondent banks (ANZ, BNP Paribas, BNY Mellon, RBC Royal Bank and Wells Fargo). The PoC is part of SWIFT’s ‘gpi’ (global payments innovation) service, the new standard for cross-border payments, aimed to “re-arm the correspondent banking system for a new age of technological disruption”. 
 While the role of the treasurer is changing, it becomes increasingly challenging to maintain the current workflows and simultaneously take on new demanding tasks. One of these often manual and time-consuming tasks is risk management. As seen in, among others, this year’s Global Treasury Benchmark Survey of PwC, the registration and management of financial instruments stands among the top 3 challenges on the agenda of the surveyed treasurers. In this article, we take a more in-depth look at possible optimizations in some key treasury workflows.
While the role of the treasurer is changing, it becomes increasingly challenging to maintain the current workflows and simultaneously take on new demanding tasks. One of these often manual and time-consuming tasks is risk management. As seen in, among others, this year’s Global Treasury Benchmark Survey of PwC, the registration and management of financial instruments stands among the top 3 challenges on the agenda of the surveyed treasurers. In this article, we take a more in-depth look at possible optimizations in some key treasury workflows.

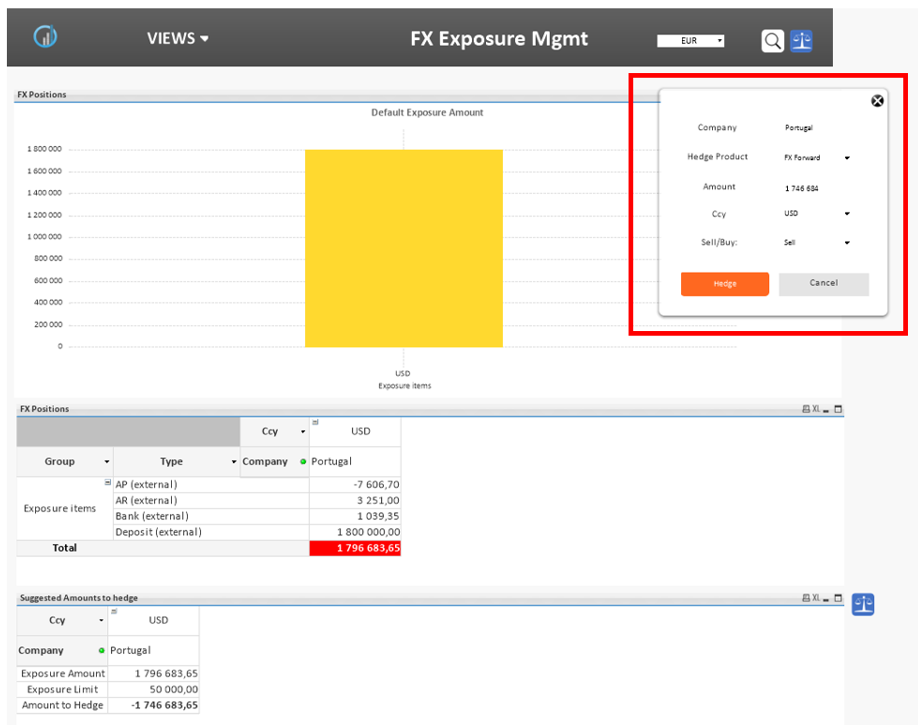
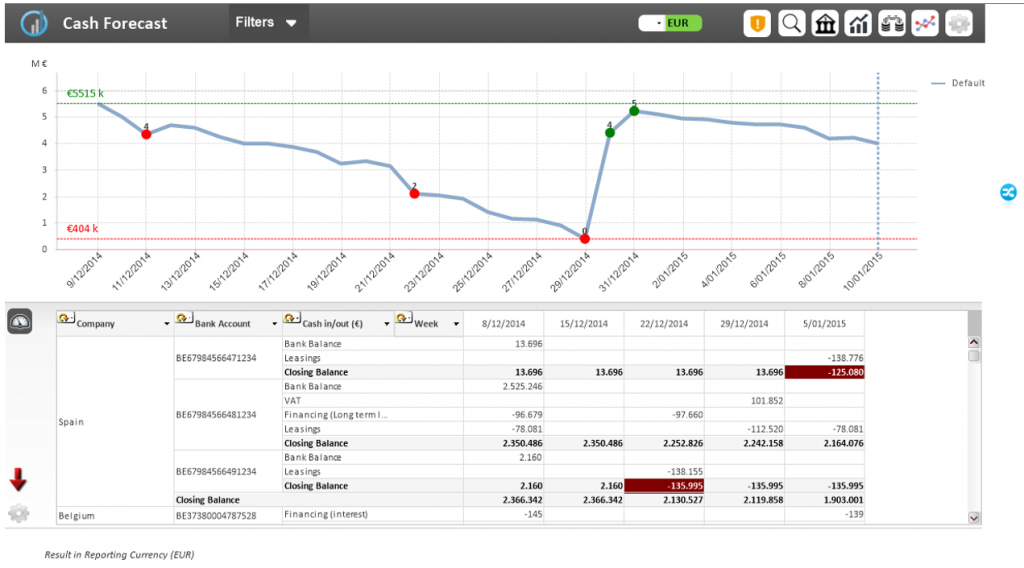
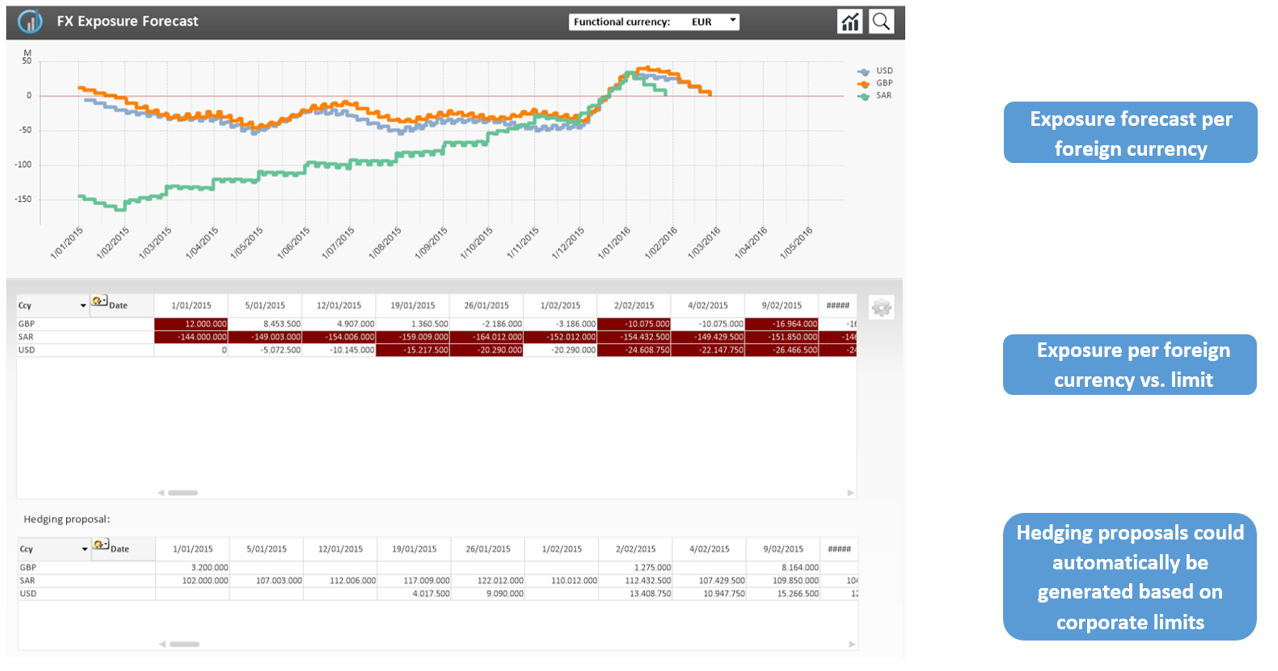 FX Exposure Management – Future positions & exposures
FX Exposure Management – Future positions & exposures

 Banks have long been target of wild spread ideas that their role as facilitator in the (inter) national money transaction industry will soon be overtaken by new Fintech initiatives like PayPal, Bitcoin and recently Ethereum. The idea behind these new technologies is that the Trusted Third Party (TTP) role of the conventional banks which is crucial for the operational day to day operations of the economic systems can be overtaken by the new block chain technology. Main advantages are clear: transactions are no longer limited by timing (no dependency on the operational boundaries of clearing houses, cut-off times of banks per currency, immediate processing etc), account opening procedures at the banks, the costs involved in maintaining accounts and transactions themselves etc.
Banks have long been target of wild spread ideas that their role as facilitator in the (inter) national money transaction industry will soon be overtaken by new Fintech initiatives like PayPal, Bitcoin and recently Ethereum. The idea behind these new technologies is that the Trusted Third Party (TTP) role of the conventional banks which is crucial for the operational day to day operations of the economic systems can be overtaken by the new block chain technology. Main advantages are clear: transactions are no longer limited by timing (no dependency on the operational boundaries of clearing houses, cut-off times of banks per currency, immediate processing etc), account opening procedures at the banks, the costs involved in maintaining accounts and transactions themselves etc.

 As financial technologies develop, bank independency is something more and more companies adopt. Bank independency not only means that financial streams are dealt with online and require less manual interventions (straight through processing). Mainly not having to rely on the services provided by the bank where the account is held is also an important one when talking about bank independency. A couple of things mentioned below emphasise the importance of being, or becoming, bank independent.
As financial technologies develop, bank independency is something more and more companies adopt. Bank independency not only means that financial streams are dealt with online and require less manual interventions (straight through processing). Mainly not having to rely on the services provided by the bank where the account is held is also an important one when talking about bank independency. A couple of things mentioned below emphasise the importance of being, or becoming, bank independent. Mark van de Griendt – Cash Management Expert at
Mark van de Griendt – Cash Management Expert at  In his article ‘
In his article ‘ Last weeks the payment service providers (PSPs)
Last weeks the payment service providers (PSPs) 



