Duplicate Payments: Instability with Multiple Platforms
| 24-06-2019 | BELLIN |
It is an arduous request for your Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) payment platforms or IT department to provide ample protection against duplicate payments and cyber-fraud. Though it can be tempting to assume administrative controls can provide protection, the facts can show otherwise. Supplier invoice payments are typically the largest annual payments and consequently, represent the highest amount of risk.
According to an Acculytic’s report on duplicate payments, “industry studies have shown that the rate of duplicate payments can be as high as 3%. In fact, 20% of the best performing companies, responding to the 2013 ePayables survey performed by Ardent Partners, had an average duplicate payment rate over 1%.”
Acculytic’s report also stated that “the Institute of Finance & Management (IOFM) concluded that a quarter of the respondents reported duplicate payment rates between 0.1% and 0.5%. Applying these rates to different purchase volumes suggests the following rate of duplicate payments may be generally applied across all organizations.”
| Rate of Duplicate Payments ($) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Purchase Volume | 0.1% | 0.5% | 1.0% |
| $10,000,000 | 10,000 | 50,000 | 100,000 |
| $50,000,000 | 50,000 | 250,000 | 500,000 |
| $100,000,000 | 100,000 | 500,000 | 1,000,000 |
How duplicate payments and payment fraud can bypass controls
Even the most sophisticated controls still have their pain points. Here are 5 ways that duplicate payments and fraud can unhinge even the best administrative controls:
1) Human error transcends even the most secure systems.
Regardless of how technologically-sound and secure an ERP or IT infrastructure is, mistakes can always occur. Such systems can typically alert when duplicate payments occur by executing matching runs. However, matching runs are incapable of determining if there was an error earlier in the submission phase.
2) Multiple systems leading to inefficiency
The presence of multiple systems is not rare with large multinational organizations. Payment processing becomes more complex in terms of ensuring ample security is present. The seamless connectivity between all systems is a paramount function to be able to detect duplicate payments.
3) Platform migration limbo period presents payment risk
When migrating from one platform to another, there is often a period in which one platform is introduced before the initial is removed. That period before the legacy platform is removed causes a risk for duplicate payments.
4) Administrative controls: biggest strength is a potential weakness
Automation comes with pros and cons and is effective with routine tasks but your integrated controls systems can hamper the speed and efficiency of your productivity. Duplicate payments are detected based on the parameters set and if there are too many parameters, a majority of payments will be flagged. With too few parameters, duplicate payments will slip through the cracks.
5) Accounts Payable are susceptible to internal fraud
Automated detection is a first line of defense but cannot factor in employees that are extremely familiar with the parameters and know how to evade detection. Invoices under certain amounts tend to not require secondary approval, leading to undetected invoices being processed.
3 essential ways a centralized platform can prevent duplicate payments
- Seamless data extraction for routine analysis that will not slow operations.
- Ability to consolidate and analyze data from any subsidiary or location.
- Digestible data that is concise with the system providing relevant alerts for fraud or issues in payment processing.
Bonus function: the ability to analyze historical payments and check for duplicate payments, tax or currency problems, contractual compliance, etc.
Eliminate duplicate payments with a centralized platform
For comprehensive protection, BELLIN’s treasury management system, tm5, will seamlessly connect all of your banks and enable you to process payments and view master vendor information. The centralized platform allows you to connect any system to any bank giving you a true, single-window view of your worldwide banking data.
With company-wide visibility as a core competency of tm5, users can monitor payment and vendor information through the entire workflow. Consequently reducing the chance for duplicate payments that originate from external or internal sources.
Treasury management systems are both innovative and extremely helpful. Knowing this, treasurers are tasked with realizing and dealing with the limitations of having multiple systems. Centralizing payment processes with automation that ensures security is an extremely efficient way to maximize controls and minimize the chance for duplicate payments to occur.



 Presenter
Presenter

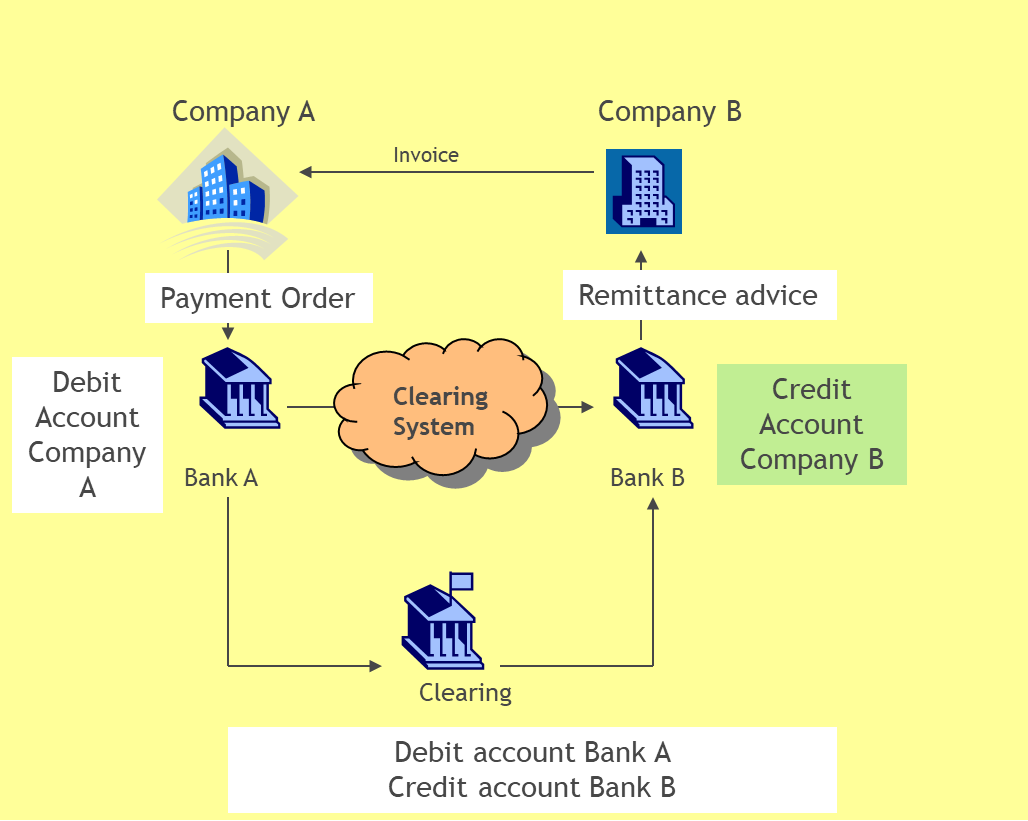
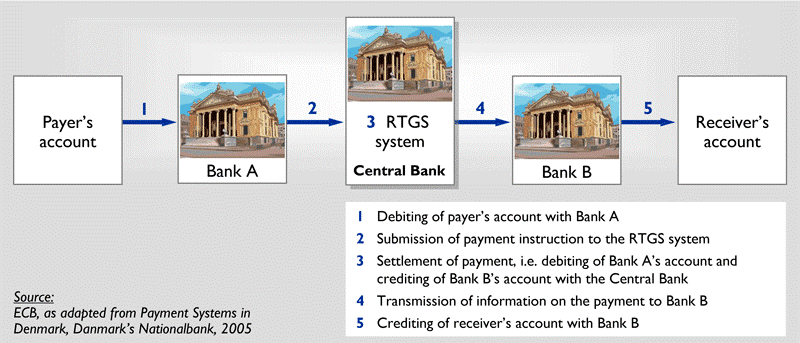
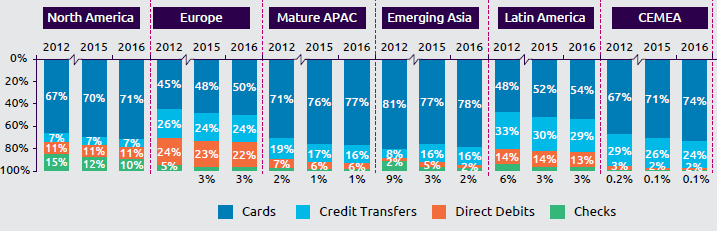


 Wat is er gebeurd met de Bitcoin per 1 augustus? De Bitcoin is gesplitst! Ik zal het hieronder proberen uit te leggen. Ik voorspel u vast, het is niet eenvoudig. Na de vele discussies over de schaal van de digitale valuta Bitcoin, is er besloten om een geheel nieuwe valuta te maken, de Bitcoin Cash. Het is wel een beetje ingewikkeld allemaal. Het is een resultaat van politieke, technologische en ideologische discussies over het laten groeien van de Bitcoin. Sommige deskundigen zeggen dat een hele nieuwe valuta, genaamd Bitcoin Cash, kan helpen om Bitcoin op grotere schaal toegankelijk te maken voor een grotere groep mensen.
Wat is er gebeurd met de Bitcoin per 1 augustus? De Bitcoin is gesplitst! Ik zal het hieronder proberen uit te leggen. Ik voorspel u vast, het is niet eenvoudig. Na de vele discussies over de schaal van de digitale valuta Bitcoin, is er besloten om een geheel nieuwe valuta te maken, de Bitcoin Cash. Het is wel een beetje ingewikkeld allemaal. Het is een resultaat van politieke, technologische en ideologische discussies over het laten groeien van de Bitcoin. Sommige deskundigen zeggen dat een hele nieuwe valuta, genaamd Bitcoin Cash, kan helpen om Bitcoin op grotere schaal toegankelijk te maken voor een grotere groep mensen.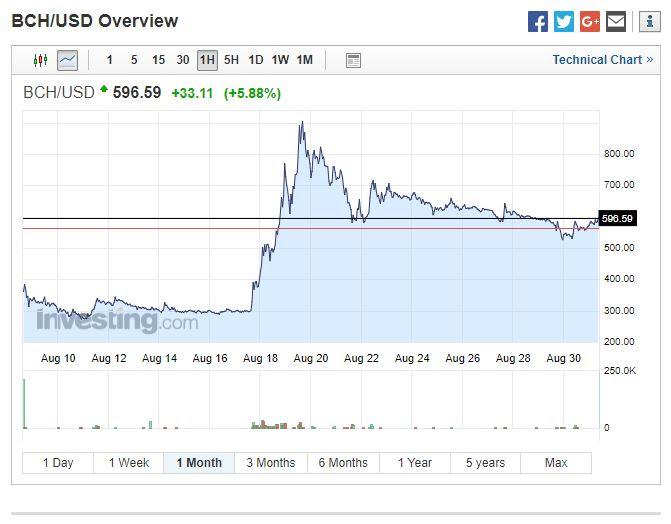




 Proferus
Proferus Cashforce Cash forecasting 2.0
Cashforce Cash forecasting 2.0