Option Tales: ATM or OTM?
 10-05-2016 | By Rob Soentken |
10-05-2016 | By Rob Soentken |
When uncertainty is substantial and the decision was made to hedge with options, should the strike be put ‘At The Money’ (ATM) or ‘Out of The Money’ (OTM)? Diagram 1 shows the dilemma.
An ATM call option on USD with strike at 1.1400 costs about 2% while a 4% OTM option with the strike at 1.0944 costs only about 0.6%. The latter is substantially cheaper but the protection only kicks in once the USD has appreciated 4%.
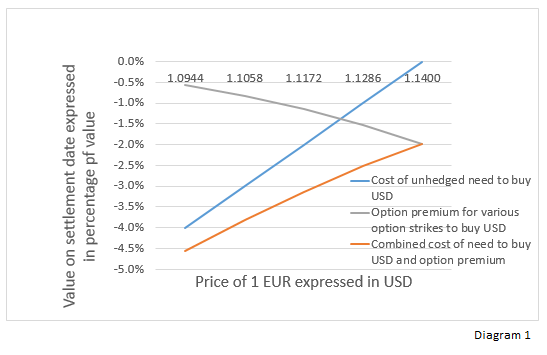
We know the premiums and the strikes, but each strike / premium combination has its merits. It would help if we would know the amount of Risk we are running. To speak in terms of insurance: We know the premium, but we do not know the potential loss. One thing we do know is the chance on that loss. This chance factor is called Delta. It is the chance of the USD appreciating below the strike of the option. The premium divided by the chance on the loss is the potential loss. It could be more, it could be less, but it is the estimated average loss. For example: The 1.14 strike costs 2% premium and has a 50% chance of being worth anything. Therefore the 2% is the premium on an insurance contract potentially worth 2% : 50% = 4%. Lets call this Risk.
Diagram 2 shows Premiums, Delta and Risk for various OTM strikes.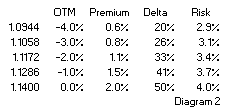 Risk appears fairly stabile across strikes, which makes sense because the premiums are calculated with one volatility on one underlying. The Risk on OTM is lower than that for ATM options. It appears that OTM premiums are relatively more expensive, they give protection against less potential loss.
Risk appears fairly stabile across strikes, which makes sense because the premiums are calculated with one volatility on one underlying. The Risk on OTM is lower than that for ATM options. It appears that OTM premiums are relatively more expensive, they give protection against less potential loss.
Knowing the Risk to be around 3.5-4% on the USD to be purchased, it does not come as a surprise that in real life many option strikes are bought to protect for losses beyond this percentage amount. Hedgers are looking for protection beyond the expected potential loss on the underlying. These are OTM strikes in this case 3-4% OTM, with a Delta (chance of exercise) between 20-25%.
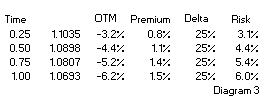 Diagram 3 shows Premiums, Delta and Risk for different tenors. ‘Time’ is the time to expiry of the options in fractions of years. Its shows that for longer tenors, the Risk is higher. But disproportionally. For the same chance on exercise a hedger could double the premium to buy a hedge for a 4x longer tenor.
Diagram 3 shows Premiums, Delta and Risk for different tenors. ‘Time’ is the time to expiry of the options in fractions of years. Its shows that for longer tenors, the Risk is higher. But disproportionally. For the same chance on exercise a hedger could double the premium to buy a hedge for a 4x longer tenor.

Ex-derivatives trader










