An Introduction to Forwards, Futures and Options | Part 1
03-06-2020 | by Aastha Tomar
Our financial world has now gone through enough crisis. Some learnt from previous crisis and were braced for the next while some were still in their learning phase. The current crisis took everyone by alteration because this time it was not the financial sector which was responsible for the ordain. The fluctuations seen in equity, bond, commodity and currency markets may have become Achilles heels for Corporate Treasurers in current times.
The incumbent state of affairs was such that Corporates had to protect their bottom line while trying to stay afloat. The entire cash flow projections would have gone for a flip for those who didn’t hedge their foreign currency exposure. One way that would have taken a part of vexation away from corporate treasurers due to currency fluctuation is hedging. It would have attenuated the impact of currency fluctuation on investments, borrowings, assets etc .
Let us have a look at the most used and basic methods of hedging in this article :
Forwards
So what are forwards? In a simple language its a hedge product between two parties which freezes your cash flow for a future date. That ways whatever the market situation be on the maturity date of the hedge, your cash flows are locked and predetermined. Whether you are an exporter who can know the exact value of future payments or an importer who can anticipate the exact costs of products; a forward will hedge the risk of currency fluctuation for both.
Features of Forwards :
- Specifies the amount, date and rate for a future currency exchange
- Parties involved are banks and businesses with foreign currency exposure
- They are over the counter products
- They can be customized
- They need two parties, one buyer other a seller
- There is no upfront payment
- Determining a currency forward rate depends on interest rate differentials for the currency pair in question
Example :
Suppose you are an exporter based in the Netherlands and you want to sell Dollars in an years time. You know due to current euro zone, corona crisis and negative interest rate scenarios Euro may fluctuate sideways and therefore you want to lock in the price of USD today itself so that one year down the line you don’t have to worry about the fluctuating rates. What do you do ? You approach a bank informing them that you have to sell USD (buy EURUSD) for 1st June, 2021. After basic documentation bank enters with an forward agreement with you . Where in today’s spot rate , the currency premium for one year , the amount of hedge and the maturity rate will be mentioned .
Spot EURUSD : 1.08282 (1 EUR = 1.08282 USD )
1 year interest rate for EUR = -.07%
1 year interest rate for USD = 0.7%
So after one year based on interest rate parity :
EUR 1* ( 1+(-.0007))= USD 1.08282 *( 1+ .007)
0.9993 EUR = 1.090 USD
Therefore 1 EUR = 1.0911 USD
Therefore by entering a forward contract today you have fixed your EURUSD rate to 1.0911. Note that because the dollar has a higher interest rate than the EUR, it trades at a forward discount to the EUR.
Let us take a simple scenario analysis to make things clearer :
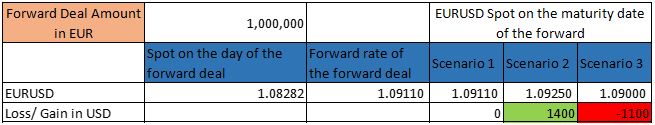
Here the forward deal amount is : EUR 1mn
Spot rate on the day of deal is : 1.08282
Forward rate fixed for the deal is : 1.0911
We can clearly see above that if the spot is same as the forward rate on the maturity date then there is no loss or gain, but if spot moves to 1.09250 then the corporate saves USD 1400 on the contrary if spot moves to 1.0900 the corporate wont be able to take advantage of the low price and will have to exercise the forward at 1.0911 as fixed earlier thus letting go of USD 1100.
So if forwards are so beneficial why do corporates still do not execute forwards for all of their foreign currency transactions :
- There is some documentation involved and corporates sometimes feel that its time taking and taxing
- At maturity date what so ever the actual spot rate be your forward will be executed at the fixed price , and some corporates feel that they may lose a chance to take advantage of better rates.
- Banks charge a small fee for entering the transactions which corporates want to save.
- Corporates feel the currency wont fluctuate much and hence don’t want to get into forward transaction.
Whatever the reasons be but the main business of corporates is not to use their energies in managing their fx risk but to increase profits by their mainline business hence its always advised for corporates to hedge their fx risk as much as possible to increase efficiency and prevent themselves from unseen shocks.
In our next post in this series we will see a second type of hedge … to be continued. Till then keep learning and be safe .
FX & Derivatives | Debt Capital Markets | MBA Finance
Electrical Engineer | Sustainability