| 1-2-2017 | François de Witte |
 After having examined the detailed measures of the PSD2 in my first article, in the 2nd part we will examine the impact of PSD 2 on the market. In order to help you read the text we will once more start with a list of abbreviations.
After having examined the detailed measures of the PSD2 in my first article, in the 2nd part we will examine the impact of PSD 2 on the market. In order to help you read the text we will once more start with a list of abbreviations.
LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS USED IN THIS ARTICLE
2FA : Two-factor authentication
AISP : Account Information Service Provider
API : Application Programming Interface
ASPSP : Account Servicing Payment Service Provider
EBA : European Banking Authority
PISP : Payment Initiation Service Provider
PSD1: Payment Services Directive 2007/64/EC
PSD2 : Revised Payment Services Directive (EU) 2015/2366
PSP : Payment Service Provider
PSU: Payment Service User
RTS : Regulatory Technical Standards (to be issued by the EBA)
SCA : Strong Customer Authentication
TPP : Third Party Provider
Impact on the market
A major implementation journey:
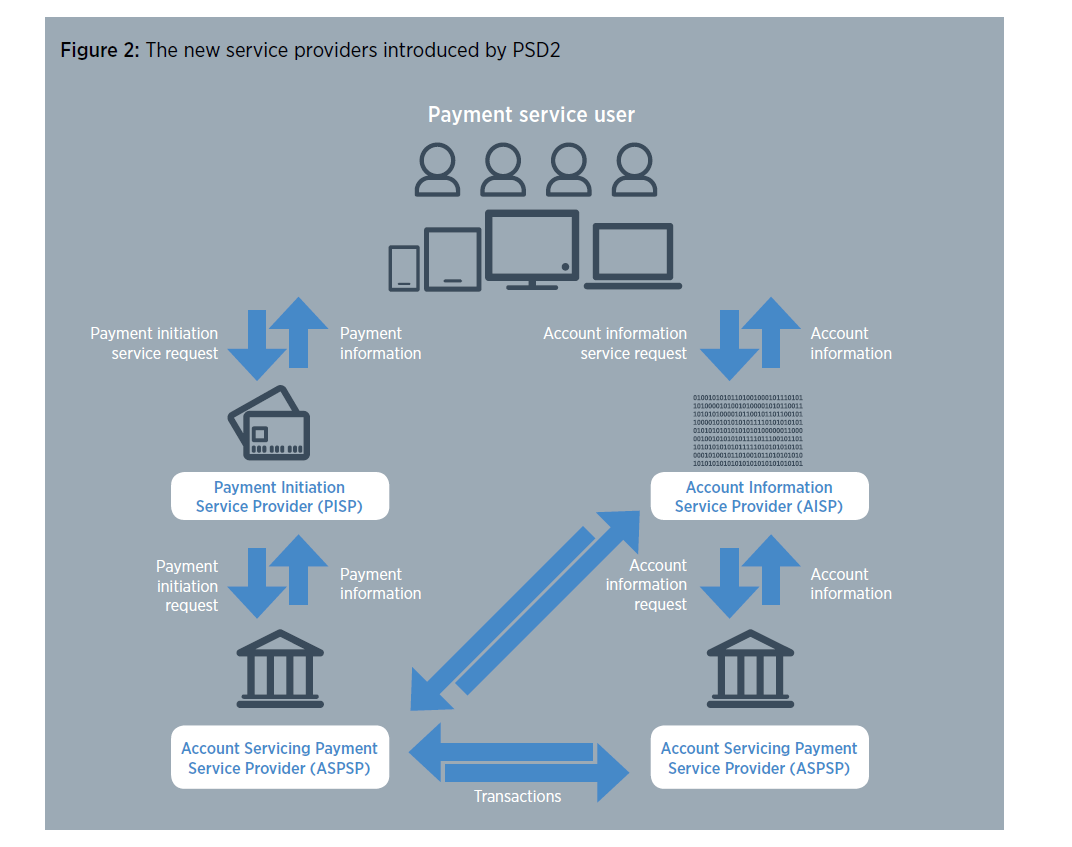
The ASPSP (mostly banks) will have to make large investments in order to comply with the PSD2, in the following fields:
- Implementing the infrastructure enabling the application of the PSD2 scheme to the currency transaction in the EU/EEA area, and to the one leg transactions.
- Ensuring that they can respond to requests for payment initiation and account information from authorized and registered TPPs (third party providers), who have received the explicit consent of their customer for to this. They will have to develop interfaces that enable third party developers to build applications and services around a bank. Internal banking IT systems might need to be able to cope with huge volumes of requests for information and transactions, more than they were originally designed for.
- Ensuring their security meets the requirements of the SCA (strong customer authentication). This will be a big challenge both for the banks and for the other payment service providers).
PSD2 will make significant demands on the IT infrastructures of banks. On the one hand the IT infrastructure has to be able to be interact with applications developed by the TPPs (PISP and AISP). On the other hand, banks have to develop their systems in such a way that they don’t have to do this from scratch every time a TPP approaches them. This will require a very flexible IT architecture. The banks have to have a middleware that can be used by their internal systems, but also by the applications of the PSP’s.
Although PSD2 does not specifically mention the API (Application Programming Interfaces), most technology and finance professionals assume that APIs will be the technological standard used to allow banks to comply with the regulation.
An API is a set of commands, routines, protocols and tools which can be used to develop interfacing programs. APIs define how different applications communicate with each other, making available certain data from a particular program in a way that enables other applications to use that data. Through an API, a third party application can make a request with standardized input towards another application and get that second application to perform an operation and deliver a standardized output back to the first application. For example, approved third parties can access your payment account information if mandated by the user and initiate payment transfer directly.
In this framework, the real challenge is to create standards for the APIs specifying the nomenclature, access protocols and authentication, etc.”. Banks will have to think about how their new API layers interact with their core banking systems and the data models that are implemented alongside this. The EBA (European Banking Authority) will develop RTS (Regulatory Technical Standard) with more detailed requirements regarding the interface between ASPSPs and TPPs. While these are expected to be published early 2017, based on the EBA’s recent draft RTS, the question is whether they will define the interface’s technical specifications.
Emergence of new players and business models
By integrating the role of new third party payment service providers (TPPs) such as the PISP and the AISP, the PSD2 creates a level playing field in the market. Several market experts expect that this will foster innovation and creating new services. For this reason PSD2 should increase competition.
This might lead to a unique open race between traditional players, such as the banks and newcomers for new services and a possible disintermediation of banking services, as illustrated in the figure down below:
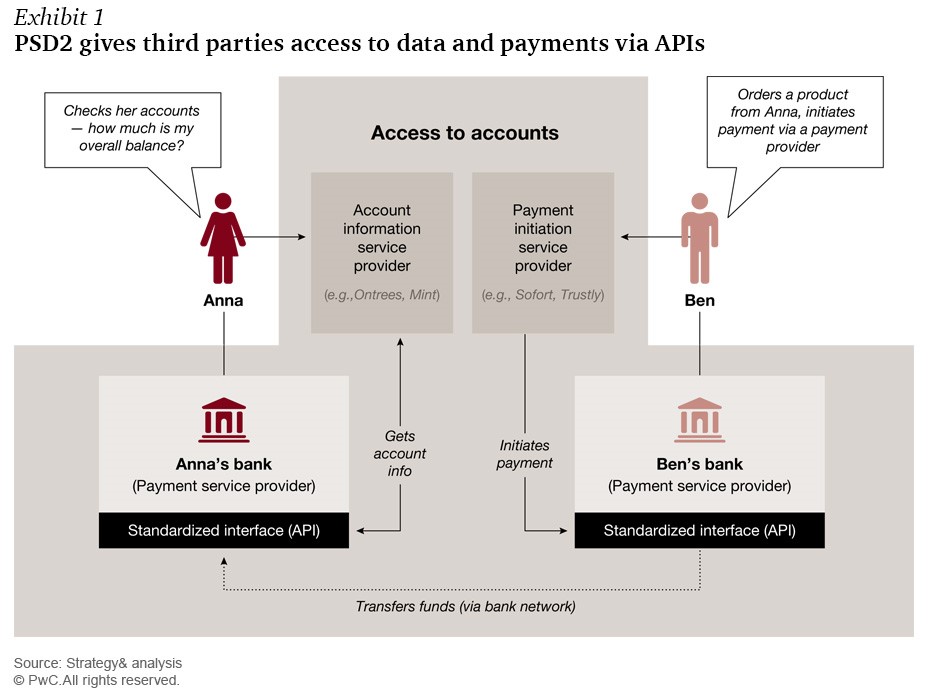
Source: Catalyst or threat? The strategic implications of PSD2 for Europe’s banks, by Jörg Sandrock, Alexandra Firnges – http://www.strategyand.pwc.com/reports/catalyst-or-threat
PSD2 is likely to give a boost to the ongoing innovation boom and bring customers more user-friendly services through digital integration. One can expect that the automation, efficiency and competition will also keep the service pricing reasonable. PSD2 will foster improved service offerings to all customer types, especially those operating in the e-commerce area for payment collection. It will enable a simpler management of accounts and transactions. New offerings may also provide deeper integration of ERP functions with financial services, including of their multibank account details under a single portal, and smart dashboards.
PSD2 also enables a simplified processing chain in which the card network can be disintermediated. The payment can be initiated by the PISP directly from the customer’s bank account through an interface with the ASPSP. In this scheme, all interchange fees and acquirer fees as well as all the fees received by the processor and card network could be avoided. The market expects that new PISPs will be able to replace partly the transactions of the classic card schemes. A large internet retailer could for example ask permission to the consumers permitting direct account access for payment. They could propose incentive to encourage customers do so. Once permission is granted then the third-parties could bypass existing card schemes and push payments directly to their own accounts.
On the reporting side, the AISP can aggregate consumer financial data and provide consumers with direct money management services. They can be used as multi-bank online electronic banking channel. One can easily imagine that these services will be able to disintermediate existing financial services providers to identify consumer requirements and directly offer them additional products, such as loans and mortgages.
The PSD2 is for banks a compliance subject, but also an opportunity to develop their next generation digital strategy. New TPPs can provide their innovative service offerings and agility to adopt new technologies, enabling to create winning payments propositions for the customer. In turn, traditional players like banks can bring their large customer bases, their reach and credibility. Banks have also broad and deep proven data handling and holding capabilities. This can create winning payments propositions for the customer, the bank and the TPP.
Banks will have to decide whether to merely stick to a compliance approach, or to leverage on the PSD2 to develop these new services. The second approach will require to leave behind the rigid legacy structures and to change their mindset to ensure quicker adaption to the dynamic customer and market conditions. A first mover strategy can prove to be beneficial. Consumers and businesses will be confronted with the increased complexity linked to the multitude of disparate offerings. There also, the incumbent banks who will develop new services can bring added value as trusted partners
Essentially, PSD2 drives down the barriers to entry for new competitors in the banking industry and gives new service providers the potential to attack the banks and disintermediate in one of their primary customer contact points. New players backed by strong investors are ready to give incumbents a serious run for their business. This is an important battle that the incumbent banks are not willing to lose.
The biggest potential benefits will be for the customers, who can access new value propositions, services and solutions that result from banks and new entrants combining their individual strengths or from banks becoming more innovative in the face of increased competition. Market experts also foresee an increased use of online shopping and e-procurement.
Several challenges to overcome
The PSD2 will be transposed in the national legal system of all the member countries. The involved market participants will have to examine the local legislation of their country of incorporation, as there might be some country-based deviations.
The authentication procedure is also an important hot topic. PISPs and AISPs can rely on the authentication procedures provided by the ASPSP (e.g. the banks) to the customer but there are customer protection rules in place. Hence, they must ensure that the personalized security credentials are not shared with other parties. They also may not store sensitive payment data, and they are obliged to identify themselves to the ASPSP each time a payment is initiated or data is exchanged.
ASPSPs are required according to PS2 to treat payment orders and data requests transmitted via a PISP or AISP “without any discrimination other than for objective reasons”. A practical consequence for credit institutions will be that they must carry out risk assessments prior to granting payment institutions access – taking into account settlement risk, operational risk and business risk. One of the main issue is the handling of the customer’s bank credentials by third party payment service providers. The bank needs to be able to perform strong authentication to ensure that the authorized account user is behind the initiation message
There are concerns about security aspects related to PSD2. An example hereof is the secure authentication. All the PSPs will have to ensure that they can demonstrate compliance with the new security requirements. How it will be achieved and monitored ? How will TPPs interact with banks, since there is no need for a contract to be signed?
If something does not work correctly, there will also be discussions on the liability side. The PSD2 states that the TPP has to reimburse customers quickly enough that they are not bearing undue risk, but one will have to determine which TPP had the problem and work with them to resolve it. This will require further clarifications from the regulators.
In addition the PISP and the AISP vulnerable for to potential frauds. Web and mobile applications could become easy target for cybercriminals for various reasons, including the inherent vulnerabilities in the APIs that transfer data and communicate with back-end systems. The openness of the web could allow hackers to view source code and data and learn how to attack it. APIs have been compromised in several high-profile attacks that have caused significant losses and embarrassment for well-known players and their customers. The PSD2’s ‘access to account’ increases not only the number of APIs, but adds layers of complexity to the online banking/payments environment, adding to the risk of fraudulent attacks.
The market is waiting for the RTS (Regulatory Technical Standards) to give guidance on how some remaining security issues will be solved. These include:
- Treatment of PSU’s (payment service user)security credentials
- Requirements for secure communication between the PSP and banks
- Full details and definition of strong authentication
- Safety of the PSU funds and personal data
- Availability of license registry for real-time identification of the PSP (PISP or AISP)
It is important that the required clarifications are published soon, in order to avoid a time lag between the implementation of PSD 2 in the national legislations and the real move in the market.
Conclusion
The PSD2 creates challenges, such as the huge investments to be made by the banks, compliance issues and protection against fraud and cybercrime. However several topics need to be clarified such as the RTS and the market players need also to agree on common standards for the interfaces. The clock is ticking in the PSD race.
Traditional players such as the banks appear to have a competitive disadvantage vis-à-vis the new emerging third party payment service providers. However, the Directive opens up new forms of a collaborative approach that can overcome this. New players can provide their innovation and resilience, whilst banks can add value thanks to their large customer base, credibility, reach and ability to cope with high volumes.
The biggest potential benefits might be for customers, who will benefit from new value propositions, services and solutions from new entrants, from banks and new entrants combining their individual strengths, or from banks becoming more innovative in the face of increased and agile competition.
 François de Witte – Senior Consultant at FDW Consult
François de Witte – Senior Consultant at FDW Consult
[button url=”https://www.treasuryxl.com/community/experts/francois-de-witte/” text=”View expert profile” size=”small” type=”primary” icon=”” external=”1″]
[separator type=”” size=”” icon=””]
 Like last year The PAYPERS releases a dedicated guide with global insights on the transaction banking, B2B payments, supply chain finance & e-invoicing market. The pages of this year`s edition keep the vibrant and dynamic atmosphere of the banking & payments industry they shared with you in previous editions.
Like last year The PAYPERS releases a dedicated guide with global insights on the transaction banking, B2B payments, supply chain finance & e-invoicing market. The pages of this year`s edition keep the vibrant and dynamic atmosphere of the banking & payments industry they shared with you in previous editions.
 After having examined the detailed measures of the PSD2 in my
After having examined the detailed measures of the PSD2 in my
 François de Witte – Senior Consultant at
François de Witte – Senior Consultant at