An Introduction to Forwards, Futures and Options | Part 2
17-06-2020 | by Aastha Tomar
In her previous post, our Expert Aastha Tomar explained how the forwards work. Lets see the second type of hedge. The second type of hedge contract is futures. Like forwards they also fix the currency rate for a future date. The major difference between a future and a forward is that futures are exchange traded and therefore they are standardized.
Features of Futures
- They have standard sizes, delivery dates and settlement rules. The settlement mechanisms reduces much of the credit risk .
-> Now why do I say that credit risk is reduced ? As mentioned earlier, all settlement takes place through the exchange clearing house and the two parties buyer and seller are not in direct contact with each other. Therefore since it is the responsibility of exchange clearing house to settle the trade, the counter-parties run the credit risk of the exchange clearing house instead on each other. - They can be cash settled or physically delivered and are legally binding.They trade in one contract size, so corporate must trade in multiples of that
- They move in increments called ticks and each tick has a value. The number of ticks made or lost on a trade determines the loss/profit of the trade
- The counter parties holding the contracts on the expiration date must deliver the currency amount at the specified price on the specified delivery date or they can even close out the position before the expiry date, this can be done by doing an equal and opposite trade in the same futures contract.
- To enter into a future contract an initial deposit into a margin account is required . The contract is then marked to market each day and a company is required to add more funds to the margin account if cumulative losses drain the margin account. If the company does not respond to a margin call, the exchange closes out the contract.
- The contracts are physically delivered four times in a year on the third Wednesday of March, June, September, and December.
Difference between future and forwards
- Futures are traded on an exchange hence standardized therefore a company may not be able to hedge the exact and full amount of underlying transaction. They may have to under-hedge .
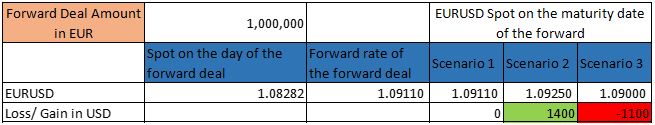
- The delivery date in future may not be same as the maturity of underlying transaction which may open the corporate for some market fluctuation.
- The treasures can easily unwind a hedge position earlier than its normal settlement date if needed.
- In a forward contract, the bank includes a transaction fee in the contract. In a futures contract, a broker charges a commission to execute the deal.
Lets understand futures with an example :
Lets take EUR/USD as an example,
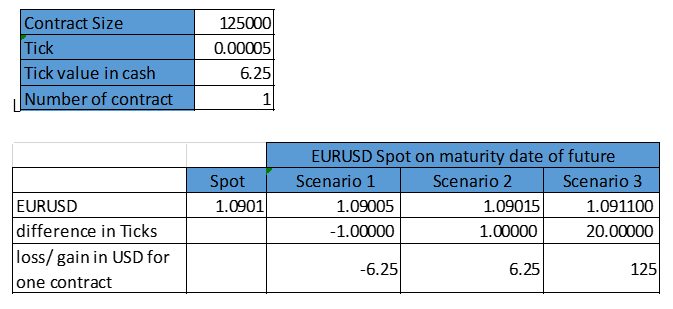
One contract size for EURUSD future is $125,000 worth of Euros and one tick size for EURUSD future is .00005. Therefore the price movement will be ($125,000*.00005) =$6.25 per EUR
Now if we purchase one futures contract of the EUR/USD, which is trading $1.0901 . We are hoping that EUR will appreciate , relative to the Dollar. Suppose we are lucky and things go as expected, and the exchange rate rises to $1.09015, We will make $6.25 in profit (per contract). Cool !!! Suppose we are luckier and FED makes some negative announcement on top of that ECB does some tremendous positive changes in their policy due to which EUR shoots up becomes much more stronger and exchange rate rises to $1.09110 (a whooping increase of 20 ticks), then we would make $125.00 in profit per contract ($6.25 x 20 ticks = $125.00).
lets see it more clearly in the following table :
Now why do corporates stay away from Futures ?
- Futures cannot be customized hence there is not always a complete hedge
- Companies don’t want to put initial margin money in the exchange
- They want to stay away from the hassle of mark to market each day and depositing money if the losses erase the deposited margin money
- With forwards there is a human interaction with the banker who enters trade with you and you feel more comfortable with that, you may also negotiate forward premia with the banker and if there is a long standing relationship with the bank, the bank sometimes forego or reduce the fees. In Futures that’s not the case.
Whether its a forward or future contract, nothing is difficult if you have the intent to learn the product . Once you start understanding how hedge market works and start realizing the benefit of it then it will eventually be beneficial for you as a Treasurer and for your corporate which will be saved from unwanted currency fluctuations. In our third and last post in this series we will talk about Options ..keep learning, be safe.. to be continued ….
FX & Derivatives | Debt Capital Markets | MBA Finance
Electrical Engineer | Sustainability